The role of gene fusions in the evolution of metabolic pathways: the histidine biosynthesis case
- PMID: 17767732
- PMCID: PMC1963479
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2148-7-S2-S4
The role of gene fusions in the evolution of metabolic pathways: the histidine biosynthesis case
Abstract
Background: Histidine biosynthesis is one of the best characterized anabolic pathways. There is a large body of genetic and biochemical information available, including operon structure, gene expression, and increasingly larger sequence databases. For over forty years this pathway has been the subject of extensive studies, mainly in Escherichia coli and Salmonella enterica, in both of which details of histidine biosynthesis appear to be identical. In these two enterobacteria the pathway is unbranched, includes a number of unusual reactions, and consists of nine intermediates; his genes are arranged in a compact operon (hisGDC [NB]HAF [IE]), with three of them (hisNB, hisD and hisIE) coding for bifunctional enzymes. We performed a detailed analysis of his gene fusions in available genomes to understand the role of gene fusions in shaping this pathway.
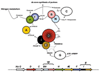
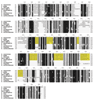
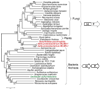
Results: The analysis of HisA structures revealed that several gene elongation events are at the root of this protein family: internal duplication have been identified by structural superposition of the modules composing the TIM-barrel protein. Several his gene fusions happened in distinct taxonomic lineages; hisNB originated within gamma-proteobacteria and after its appearance it was transferred to Campylobacter species (epsilon-proteobacteria) and to some Bacteria belonging to the CFB group. The transfer involved the entire his operon. The hisIE gene fusion was found in several taxonomic lineages and our results suggest that it probably happened several times in distinct lineages. Gene fusions involving hisIE and hisD genes (HIS4) and hisH and hisF genes (HIS7) took place in the Eukarya domain; the latter has been transferred to some delta-proteobacteria.
Conclusion: Gene duplication is the most widely known mechanism responsible for the origin and evolution of metabolic pathways; however, several other mechanisms might concur in the process of pathway assembly and gene fusion appeared to be one of the most important and common.
Figures






Similar articles
-
The origin and evolution of eucaryal HIS7 genes: from metabolon to bifunctional proteins?Gene. 2004 Sep 15;339:149-60. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2004.06.033. Gene. 2004. PMID: 15363855
-
The origin and evolution of operons: the piecewise building of the proteobacterial histidine operon.J Mol Evol. 2005 Mar;60(3):378-90. doi: 10.1007/s00239-004-0198-1. J Mol Evol. 2005. PMID: 15871048
-
Evolution of the structure and chromosomal distribution of histidine biosynthetic genes.Orig Life Evol Biosph. 1998 Oct;28(4-6):555-70. doi: 10.1023/a:1006531526299. Orig Life Evol Biosph. 1998. PMID: 9742729
-
Exploring the role of the histidine biosynthetic hisF gene in cellular metabolism and in the evolution of (ancestral) genes: from LUCA to the extant (micro)organisms.Microbiol Res. 2020 Nov;240:126555. doi: 10.1016/j.micres.2020.126555. Epub 2020 Jul 9. Microbiol Res. 2020. PMID: 32673985 Review.
-
Respiratory transformation of nitrous oxide (N2O) to dinitrogen by Bacteria and Archaea.Adv Microb Physiol. 2007;52:107-227. doi: 10.1016/S0065-2911(06)52003-X. Adv Microb Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17027372 Review.
Cited by
-
Surviving in the Brine: A Multi-Omics Approach for Understanding the Physiology of the Halophile Fungus Aspergillus sydowii at Saturated NaCl Concentration.Front Microbiol. 2022 May 2;13:840408. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.840408. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35586858 Free PMC article.
-
Structural and functional studies of histidine biosynthesis in Acanthamoeba spp. demonstrates a novel molecular arrangement and target for antimicrobials.PLoS One. 2018 Jul 3;13(7):e0198827. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0198827. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 29969448 Free PMC article.
-
Organization and evolution of the cotG and cotH genes of Bacillus subtilis.J Bacteriol. 2011 Dec;193(23):6664-73. doi: 10.1128/JB.06121-11. Epub 2011 Oct 7. J Bacteriol. 2011. PMID: 21984783 Free PMC article.
-
Helicobacter pylori GmhB enzyme involved in ADP-heptose biosynthesis pathway is essential for lipopolysaccharide biosynthesis and bacterial virulence.Virulence. 2021 Dec;12(1):1610-1628. doi: 10.1080/21505594.2021.1938449. Virulence. 2021. PMID: 34125649 Free PMC article.
-
Proteomic analysis of Acinetobacter baumannii in biofilm and planktonic growth mode.J Microbiol. 2009 Dec;47(6):728-35. doi: 10.1007/s12275-009-0158-y. Epub 2010 Feb 4. J Microbiol. 2009. PMID: 20127467
References
-
- Winkler ME. Biosynthesis of histidine. In: Neidhardt FC, Ingraham JL, Low KB, Magasanik B, Schaechter M, Humbarger HD, editor. Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium: cellular and molecular biology. Vol. 1. Washington DC: ASM Press; 1987. pp. 395–411.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

