Genetic factors in systemic sclerosis
- PMID: 17767743
- PMCID: PMC2072883
- DOI: 10.1186/ar2189
Genetic factors in systemic sclerosis
Abstract
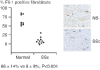
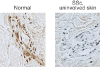
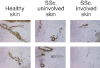
A number of genetic loci have been identified that appear to be associated with systemic sclerosis (SSc; scleroderma). There is mounting evidence suggesting that these genetic associations may in fact be associated with distinct phenotypes in SSc based on autoantibody pattern rather than with SSc as a single disease entity. This may ultimately have implications for approaches to therapy as well as responses to therapy. The most promising candidate genes are those involved in pathways that lead to the vascular damage and fibrosis that are the hallmarks of this disease. There is uncertainty, however, regarding the nature of the key pathological mechanisms that link these two disease processes. Recent studies have focused on Fli1 (friend leukaemia integration 1), a transcription factor that is found in immune cells, fibroblasts, and endothelial cells that regulates collagen gene function and angiogenesis. Fli1 is dysregulated in SSc skin and dermal blood vessels, and appears to play a pathological role in SSc skin fibrosis and vessel degeneration. Whether this dysregulation is due to genetic polymorphisms in the Fli1 pathway or to epigenetic mechanisms is not clear.
Figures
References
-
- Arnett FC, Cho M, Chatterjee S, Aguilar MB, Reveille JD, Mayes MD. Familial occurrence frequencies and relative risks for systemic sclerosis (scleroderma) in three United States cohorts. Arthritis Rheum. 2001;44:1359–1362. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(200106)44:6<1359::AID-ART228>3.0.CO;2-S. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Englert H, Small-McMahon J, Chambers P, O'Connor H, Davis K, Manolios N, White R, Dracos G, Brooks P. Familial risk estimation in systemic sclerosis. Aust N Z J Med. 1999;29:36–41. - PubMed
-
- Assassi S, Arnett FC, Reveille JD, Gourh P, Mayes MD. Clinical, immunological, and genetic features of familial systemic sclerosis. Arthritis Rheum. 2007 - PubMed
-
- Zhou X, Tan FK, Wang N, Xiong M, Maghidman S, Reveille JD, Milewicz DM, Chakraborty R, Arnett FC. Genome-wide association study for regions of systemic sclerosis susceptibility in a Choctaw Indian population with high disease prevalence. Arthritis Rheum. 2003;48:2585–2592. doi: 10.1002/art.11220. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

