Clinical trials in systemic sclerosis: lessons learned and outcomes
- PMID: 17767745
- PMCID: PMC2072887
- DOI: 10.1186/ar2191
Clinical trials in systemic sclerosis: lessons learned and outcomes
Abstract
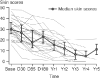
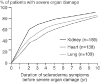
The pathogenesis of systemic sclerosis (SSc) is complex and largely unclear. The clinical heterogeneity of the disease and its progression over a number of years makes the choice of endpoints in the design of clinical trials difficult. The overwhelming need in this disease is to diagnose it early and identify those patients who will benefit most from early, aggressive treatment that potentially can alter the clinical disease course. To achieve this, innumerable challenges must be overcome. This article reviews data from recent clinical trials and the lessons derived from retrospective observational studies, databases, and patient registries. Taken together, these observations will help to improve our understanding of the diverse clinical course of SSc and permit refinement of existing outcome measures for the design of future clinical trials, in which the likelihood of observing a positive treatment effect with the drugs at our disposal will be maximized.
Figures
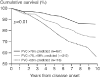
References
-
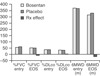
- Badesch DB, Tapson VF, McGoon MD, Brundage BH, Rubin LJ, Wigley FM, Rich S, Barst RJ, Barrett PS, Kral KM, et al. Continuous intravenous epoprostenol for pulmonary hypertension due to the scleroderma spectrum of disease. A randomized, controlled trial. Ann Intern Med. 2000;132:425–434. - PubMed
-
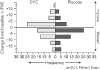
- Clements PJ, Furst DE, Wong WK, Mayes M, White B, Wigley F, Weisman MH, Barr W, Moreland LW, Medsger TA, Jr, et al. High-dose versus low-dose D-penicillamine in early diffuse systemic sclerosis: analysis of a two-year, double-blind, randomized, controlled clinical trial. Arthritis Rheum. 1999;42:1194–1203. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(199906)42:6<1194::AID-ANR16>3.0.CO;2-7. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

