Characterization of an exported monoglyceride lipase from Mycobacterium tuberculosis possibly involved in the metabolism of host cell membrane lipids
- PMID: 17784850
- PMCID: PMC2267359
- DOI: 10.1042/BJ20070745
Characterization of an exported monoglyceride lipase from Mycobacterium tuberculosis possibly involved in the metabolism of host cell membrane lipids
Abstract
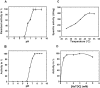
The Rv0183 gene of the Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Rv strain, which has been implicated as a lysophospholipase, was cloned and expressed in Escherichia coli. The purified Rv0183 protein did not show any activity when lysophospholipid substrates were used, but preferentially hydrolysed monoacylglycerol substrates with a specific activity of 290 units x mg(-1) at 37 degrees C. Rv0183 hydrolyses both long chain di- and triacylglycerols, as determined using the monomolecular film technique, although the turnover was lower than with MAG (monoacyl-glycerol). The enzyme shows an optimum activity at pH values ranging from 7.5 to 9.0 using mono-olein as substrate and is inactivated by serine esterase inhibitors such as E600, PMSF and tetrahydrolipstatin. The catalytic triad is composed of Ser110, Asp226 and His256 residues, as confirmed by the results of site-directed mutagenesis. Rv0183 shows 35% sequence identity with the human and mouse monoglyceride lipases and well below 15% with the other bacterial lipases characterized so far. Homologues of Rv0183 can be identified in other mycobacterial genomes such as Mycobacterium bovis, Mycobacterium smegmatis, and even Mycobacterium leprae, which is known to contain a low number of genes involved in the replication process within the host cells. The results of immunolocalization studies performed with polyclonal antibodies raised against the purified recombinant Rv0183 suggested that the enzyme was present only in the cell wall and culture medium of M. tuberculosis. Our results identify Rv0183 as the first exported lipolytic enzyme to be characterized in M. tuberculosis and suggest that Rv0183 may be involved in the degradation of the host cell lipids.
Figures
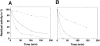

Similar articles
-
Potential selective inhibitors against Rv0183 of Mycobacterium tuberculosis targeting host lipid metabolism.Chem Biol Drug Des. 2012 Jun;79(6):1056-62. doi: 10.1111/j.1747-0285.2012.01373.x. Epub 2012 Apr 17. Chem Biol Drug Des. 2012. PMID: 22405030
-
Expression and characterization of the carboxyl esterase Rv3487c from Mycobacterium tuberculosis.Protein Expr Purif. 2005 Jul;42(1):59-66. doi: 10.1016/j.pep.2005.03.022. Epub 2005 Apr 12. Protein Expr Purif. 2005. PMID: 15939293
-
Characterization and function of Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Rv Lipase Rv1076 (LipU).Microbiol Res. 2017 Mar;196:7-16. doi: 10.1016/j.micres.2016.12.005. Epub 2016 Dec 15. Microbiol Res. 2017. PMID: 28164792
-
Lipolytic enzymes in Mycobacterium tuberculosis.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2008 Apr;78(5):741-9. doi: 10.1007/s00253-008-1397-2. Epub 2008 Feb 29. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2008. PMID: 18309478 Review.
-
Roles of Triolein and Lipolytic Protein in the Pathogenesis and Survival of Mycobacterium tuberculosis: a Novel Therapeutic Approach.Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2016 Apr;178(7):1377-89. doi: 10.1007/s12010-015-1953-z. Epub 2015 Dec 17. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2016. PMID: 26679705 Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of residues involved in substrate specificity and cytotoxicity of two closely related cutinases from Mycobacterium tuberculosis.PLoS One. 2013 Jul 2;8(7):e66913. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0066913. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23843969 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis and kinetic evaluation of cyclophostin and cyclipostins phosphonate analogs as selective and potent inhibitors of microbial lipases.J Med Chem. 2012 Nov 26;55(22):10204-19. doi: 10.1021/jm301216x. Epub 2012 Nov 7. J Med Chem. 2012. PMID: 23095026 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging mechanisms by which endocannabinoids and their derivatives modulate bacterial populations within the gut microbiome.Adv Drug Alcohol Res. 2023 Dec 8;3:11359. doi: 10.3389/adar.2023.11359. eCollection 2023. Adv Drug Alcohol Res. 2023. PMID: 38389811 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Roles of Lipolytic enzymes in Mycobacterium tuberculosis pathogenesis.Front Microbiol. 2024 Jan 29;15:1329715. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1329715. eCollection 2024. Front Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38357346 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of Lipid-Lowering Drugs on Vancomycin Susceptibility of Mycobacteria.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2016 Sep 23;60(10):6193-9. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00872-16. Print 2016 Oct. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2016. PMID: 27503643 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Daffe M., Draper P. The envelope layers of mycobacteria with reference to their pathogenicity. Adv. Microb. Physiol. 1998;39:131–203. - PubMed
-
- Minnikin D. London: Academic Press; 1982. Lipids: complex lipids, their chemistry, biosynthesis and roles.
-
- Minnikin D. E., Kremer L., Dover L. G., Besra G. S. The methyl-branched fortifications of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Chem. Biol. 2002;9:545–553. - PubMed
-
- Kremer L., de Chastellier C., Dobson G., Gibson K. J., Bifani P., Balor S., Gorvel J. P., Locht C., Minnikin D. E., Besra G. S. Identification and structural characterization of an unusual mycobacterial monomeromycolyl-diacylglycerol. Mol. Microbiol. 2005;57:1113–1126. - PubMed
-
- Dawes E. A., Senior P. J. The role and regulation of energy reserve polymers in microorganisms. Adv. Microb. Physiol. 1973;10:135–266. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

