Identification of JTP-70902, a p15(INK4b)-inductive compound, as a novel MEK1/2 inhibitor
- PMID: 17784872
- PMCID: PMC11158247
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2007.00604.x
Identification of JTP-70902, a p15(INK4b)-inductive compound, as a novel MEK1/2 inhibitor
Abstract
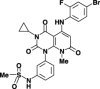
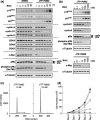
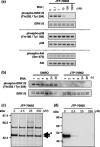
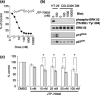
The INK4 family members p16(INK4a) and p15(INK4b) negatively regulate cell cycle progression by inhibition of cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK) 4/6. Loss of p16(INK4a) functional activity is frequently observed in tumor cells, and is thought to be one of the primary causes of carcinogenesis. In contrast, despite the biochemical similarity to p16(INK4a), the frequency of defects in p15(INK4b) was found to be lower than in p16(INK4a), suggesting that p15(INK4b)-inductive agents may be useful for tumor suppression. Here we report the discovery of a novel pyrido-pyrimidine derivative, JTP-70902, which exhibits p15(INK4b)-inducing activity in p16(INK4a)-inactivated human colon cancer HT-29 cells. JTP-70902 also induced another CDK-inhibitor, p27(KIP1), and downregulated the expression of c-Myc and cyclin D1, resulting in G(1) cell cycle arrest. MEK1/2 was identified by compound-immobilized affinity chromatography as the molecular target of JTP-70902, and this was further confirmed by the inhibitory activity of JTP-70902 against MEK1/2 in kinase assays. JTP-70902 suppressed the growth of most colorectal and some other cancer cell lines in vitro, and showed antitumor activity in an HT-29 xenograft model. However, JTP-70902 did not inhibit the growth of COLO320 DM cells; in these, constitutive extracellular signal-regulated kinase phosphorylation was not detected, and neither p15(INK4b) nor p27(KIP1) induction was observed. Moreover, p15(INK4b)-deficient mouse embryonic fibroblasts were found to be more resistant to the growth-inhibitory effect of JTP-70902 than wild-type mouse embryonic fibroblasts. These findings suggest that JTP-70902 restores CDK inhibitor-mediated cell cycle control by inhibiting MEK1/2 and exerts a potent antitumor effect.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Decreased proliferation and cell cycle arrest in neoplastic rat pituitary cells is associated with transforming growth factor-beta1-induced expression of p15/INK4B.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2001 May 15;176(1-2):29-37. doi: 10.1016/s0303-7207(01)00477-4. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2001. PMID: 11369440
-
Antitumor activities of JTP-74057 (GSK1120212), a novel MEK1/2 inhibitor, on colorectal cancer cell lines in vitro and in vivo.Int J Oncol. 2011 Jul;39(1):23-31. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2011.1015. Epub 2011 Apr 26. Int J Oncol. 2011. PMID: 21523318
-
Cellular response to oncogenic ras involves induction of the Cdk4 and Cdk6 inhibitor p15(INK4b).Mol Cell Biol. 2000 Apr;20(8):2915-25. doi: 10.1128/MCB.20.8.2915-2925.2000. Mol Cell Biol. 2000. PMID: 10733595 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic regulation of the INK4b-ARF-INK4a locus: in sickness and in health.Epigenetics. 2010 Nov-Dec;5(8):685-90. doi: 10.4161/epi.5.8.12996. Epub 2010 Nov 1. Epigenetics. 2010. PMID: 20716961 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Review of alterations of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor INK4 family genes p15, p16, p18 and p19 in human leukemia-lymphoma cells.Leukemia. 1998 Jun;12(6):845-59. doi: 10.1038/sj.leu.2401043. Leukemia. 1998. PMID: 9639410 Review.
Cited by
-
Vertical Inhibition of the RAF-MEK-ERK Cascade Induces Myogenic Differentiation, Apoptosis, and Tumor Regression in H/NRASQ61X Mutant Rhabdomyosarcoma.Mol Cancer Ther. 2022 Jan;21(1):170-183. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-21-0194. Epub 2021 Nov 4. Mol Cancer Ther. 2022. PMID: 34737198 Free PMC article.
-
Adjuvant Trametinib Delays the Outgrowth of Occult Pancreatic Cancer in a Mouse Model of Patient-Derived Liver Metastasis.Ann Surg Oncol. 2016 Jun;23(6):1993-2000. doi: 10.1245/s10434-016-5116-4. Epub 2016 Feb 4. Ann Surg Oncol. 2016. PMID: 26847682 Free PMC article.
-
A structural perspective on targeting the RTK/Ras/MAP kinase pathway in cancer.Protein Sci. 2021 Aug;30(8):1535-1553. doi: 10.1002/pro.4125. Epub 2021 May 31. Protein Sci. 2021. PMID: 34008902 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Trametinib activates endogenous neurogenesis and recovers neuropathology in a model of Alzheimer's disease.Exp Mol Med. 2023 Oct;55(10):2177-2189. doi: 10.1038/s12276-023-01073-2. Epub 2023 Oct 2. Exp Mol Med. 2023. PMID: 37779138 Free PMC article.
-
Novel MEK inhibitor trametinib and other retinoblastoma gene (RB)-reactivating agents enhance efficacy of 5-fluorouracil on human colon cancer cells.Cancer Sci. 2013 Jun;104(6):687-93. doi: 10.1111/cas.12139. Epub 2013 Apr 3. Cancer Sci. 2013. PMID: 23438367 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sherr CJ. Mammalian G1 cyclins. Cell 1993; 73: 1059–65. - PubMed
-
- Dowdy SF, Hinds PW, Louie K, Reed SI, Arnold A, Weinberg RA. Physical interaction of the retinoblastoma protein with human D cyclins. Cell 1993; 73: 499–511. - PubMed
-
- Dyson N. The regulation of E2F by pRB‐family proteins. Genes Dev 1998; 12: 2245–62. - PubMed
-
- Sebolt‐Leopold JS, Herrera R. Targeting the mitogen‐activated protein kinase cascade to treat cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 2004; 4: 937–47. - PubMed
-
- Roovers K, Assoian RK. Integrating the MAP kinase signal into the G1 phase cell cycle machinery. Bioessays 2000; 22: 818–26. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

