3D cell nuclei segmentation based on gradient flow tracking
- PMID: 17784958
- PMCID: PMC2064921
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2121-8-40
3D cell nuclei segmentation based on gradient flow tracking
Abstract
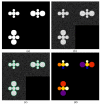
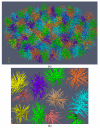
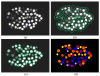
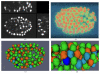
Background: Reliable segmentation of cell nuclei from three dimensional (3D) microscopic images is an important task in many biological studies. We present a novel, fully automated method for the segmentation of cell nuclei from 3D microscopic images. It was designed specifically to segment nuclei in images where the nuclei are closely juxtaposed or touching each other. The segmentation approach has three stages: 1) a gradient diffusion procedure, 2) gradient flow tracking and grouping, and 3) local adaptive thresholding.
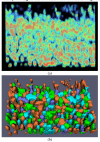
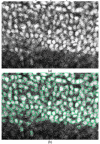
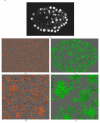
Results: Both qualitative and quantitative results on synthesized and original 3D images are provided to demonstrate the performance and generality of the proposed method. Both the over-segmentation and under-segmentation percentages of the proposed method are around 5%. The volume overlap, compared to expert manual segmentation, is consistently over 90%.
Conclusion: The proposed algorithm is able to segment closely juxtaposed or touching cell nuclei obtained from 3D microscopy imaging with reasonable accuracy.
Figures


References
-
- Jülich D, Hwee LC, Round J, Nicoliaje C, Scroeder J, Davies A, Geisler R, Lewis J, Jiang YJ, Holley SA. beamter/deltaC and the role of Notch ligands in the zebrafish somite segmentation, hindbrain neurogenesis and hypochord differentiation. Dev Biol. 2005;286:391–404. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2005.06.040. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Umesh Adiga PS, Chaudhuri BB. An efficient method based on watershed and rule-based merging for segmentation of 3-D histo-pathological images. Pattern Recognition. 2001;34:1449–1458. doi: 10.1016/S0031-3203(00)00076-5. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

