Nuclear gene silencing directs reception of long-distance mRNA silencing in Arabidopsis
- PMID: 17785412
- PMCID: PMC1964546
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0706701104
Nuclear gene silencing directs reception of long-distance mRNA silencing in Arabidopsis
Abstract
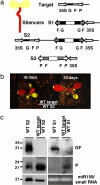
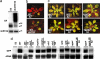
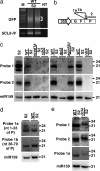
In plants, silencing of mRNA can be transmitted from cell to cell and also over longer distances from roots to shoots. To investigate the long-distance mechanism, WT and mutant shoots were grafted onto roots silenced for an mRNA. We show that three genes involved in a chromatin silencing pathway, NRPD1a encoding RNA polymerase IVa, RNA-dependent RNA polymerase 2 (RDR2), and DICER-like 3 (DCL3), are required for reception of long-distance mRNA silencing in the shoot. A mutant representing a fourth gene in the pathway, argonaute4 (ago4), was also partially compromised in the reception of silencing. This pathway produces 24-nt siRNAs and resulted in decapped RNA, a known substrate for amplification of dsRNA by RDR6. Activation of silencing in grafted shoots depended on RDR6, but no 24-nt siRNAs were detected in mutant rdr6 shoots, indicating that RDR6 also plays a role in initial signal perception. After amplification of decapped transcripts, DCL4 and DCL2 act hierarchically as they do in antiviral resistance to produce 21- and 22-nt siRNAs, respectively, and these guide mRNA degradation. Several dcl genotypes were also tested for their capacity to transmit the mobile silencing signal from the rootstock. dcl1-8 and a dcl2 dcl3 dcl4 triple mutant are compromised in micro-RNA and siRNA biogenesis, respectively, but were unaffected in signal transmission.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
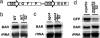
Comment in
-
Mixing and matching: the essence of plant systemic silencing?Trends Genet. 2008 Apr;24(4):151-4. doi: 10.1016/j.tig.2008.01.005. Epub 2008 Mar 5. Trends Genet. 2008. PMID: 18325623
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

