Wnt/beta-catenin is essential for intestinal homeostasis and maintenance of intestinal stem cells
- PMID: 17785439
- PMCID: PMC2169070
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.01034-07
Wnt/beta-catenin is essential for intestinal homeostasis and maintenance of intestinal stem cells
Abstract
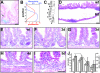
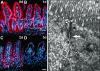
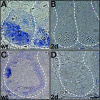
The Wnt signaling pathway is deregulated in over 90% of human colorectal cancers. beta-Catenin, the central signal transducer of the Wnt pathway, can directly modulate gene expression by interacting with transcription factors of the TCF/LEF family. In the present study we investigate the role of Wnt signaling in the homeostasis of intestinal epithelium by using tissue-specific, inducible beta-catenin gene ablation in adult mice. Block of Wnt/beta-catenin signaling resulted in rapid loss of transient-amplifying cells and crypt structures. Importantly, intestinal stem cells were induced to terminally differentiate upon deletion of beta-catenin, resulting in a complete block of intestinal homeostasis and fatal loss of intestinal function. Transcriptional profiling of mutant crypt mRNA isolated by laser capture microdissection confirmed those observations and allowed us to identify genes potentially responsible for the functional preservation of intestinal stem cells. Our data demonstrate an essential requirement of Wnt/beta-catenin signaling for the maintenance of the intestinal epithelium in the adult organism. This challenges attempts to target aberrant Wnt signaling as a new therapeutic strategy to treat colorectal cancer.
Figures



References
-
- Batlle, E., J. T. Henderson, H. Beghtel, M. M. van den Born, E. Sancho, G. Huls, J. Meeldijk, J. Robertson, M. van de Wetering, T. Pawson, and H. Clevers. 2002. Beta-catenin and TCF mediate cell positioning in the intestinal epithelium by controlling the expression of EphB/ephrinB. Cell 111: 251-263. - PubMed
-
- Behrens, J., and B. Lustig. 2004. The Wnt connection to tumorigenesis. Int. J. Dev. Biol. 48: 477-487. - PubMed
-
- Bianchini, M., E. Levy, C. Zucchini, V. Pinski, C. Macagno, P. De Sanctis, L. Valvassori, P. Carinci, and J. Mordoh. 2006. Comparative study of gene expression by cDNA microarray in human colorectal cancer tissues and normal mucosa. Int. J. Oncol. 29: 83-94. - PubMed
-
- Bjerknes, M., and H. Cheng. 1999. Clonal analysis of mouse intestinal epithelial progenitors. Gastroenterology 116: 7-14. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
