Activity of an antimicrobial peptide mimetic against planktonic and biofilm cultures of oral pathogens
- PMID: 17785509
- PMCID: PMC2151458
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.00208-07
Activity of an antimicrobial peptide mimetic against planktonic and biofilm cultures of oral pathogens
Abstract
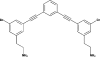
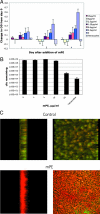
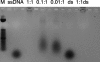
Antimicrobial peptides (AMPs) are naturally occurring, broad-spectrum antimicrobial agents that have recently been examined for their utility as therapeutic antibiotics. Unfortunately, they are expensive to produce and are often sensitive to protease digestion. To address this problem, we have examined the activity of a peptide mimetic whose design was based on the structure of magainin, exhibiting its amphiphilic structure. We demonstrate that this compound, meta-phenylene ethynylene (mPE), exhibits antimicrobial activity at nanomolar concentrations against a variety of bacterial and Candida species found in oral infections. Since Streptococcus mutans, an etiological agent of dental caries, colonizes the tooth surface and forms a biofilm, we quantified the activity of this compound against S. mutans growing under conditions that favor biofilm formation. Our results indicate that mPE can prevent the formation of a biofilm at nanomolar concentrations. Incubation with 5 nM mPE prevents further growth of the biofilm, and 100 nM mPE reduces viable bacteria in the biofilm by 3 logs. Structure-function analyses suggest that mPE inhibits the bioactivity of lipopolysaccharide and binds DNA at equimolar ratios, suggesting that it may act both as a membrane-active molecule, similar to magainin, and as an intracellular antibiotic, similar to other AMPs. We conclude that mPE and similar molecules display great potential for development as therapeutic antimicrobials.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Effects of Antimicrobial Peptide GH12 on the Cariogenic Properties and Composition of a Cariogenic Multispecies Biofilm.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2018 Nov 30;84(24):e01423-18. doi: 10.1128/AEM.01423-18. Print 2018 Dec 15. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 30341079 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of the antimicrobial decapeptide KSL on the growth of oral pathogens and Streptococcus mutans biofilm.Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2011 Jan;37(1):33-8. doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2010.08.014. Epub 2010 Oct 17. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2011. PMID: 20956070
-
A tooth-binding antimicrobial peptide to prevent the formation of dental biofilm.J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2019 Mar 30;30(4):45. doi: 10.1007/s10856-019-6246-6. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2019. PMID: 30929087
-
Antimicrobial activity of nanoemulsion on cariogenic planktonic and biofilm organisms.Arch Oral Biol. 2012 Jan;57(1):15-22. doi: 10.1016/j.archoralbio.2011.07.001. Epub 2011 Jul 31. Arch Oral Biol. 2012. PMID: 21807359 Free PMC article.
-
Small proteins and peptides conferring protection against antimicrobial compounds.Trends Microbiol. 2025 Jun;33(6):586-602. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2025.01.011. Epub 2025 Mar 6. Trends Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40055019 Review.
Cited by
-
Study of the ultrastructure of Enterococcus faecalis and Streptococcus mutans incubated with salivary antimicrobial peptides.Clin Exp Dent Res. 2021 Jun;7(3):365-375. doi: 10.1002/cre2.430. Epub 2021 May 5. Clin Exp Dent Res. 2021. PMID: 33951334 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of lipid composition on membrane activity of antimicrobial phenylene ethynylene oligomers.J Phys Chem B. 2008 Mar 20;112(11):3495-502. doi: 10.1021/jp077487j. Epub 2008 Feb 23. J Phys Chem B. 2008. PMID: 18293958 Free PMC article.
-
Cationic Amphiphilic Polymers with Antimicrobial Activity for Oral Care Applications: Eradication of S. mutans Biofilm.Biomacromolecules. 2017 Jan 9;18(1):257-265. doi: 10.1021/acs.biomac.6b01598. Epub 2016 Dec 19. Biomacromolecules. 2017. PMID: 27992189 Free PMC article.
-
The structure of nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae SapA in a closed conformation reveals a constricted ligand-binding cavity and a novel RNA binding motif.PLoS One. 2021 Oct 15;16(10):e0256070. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0256070. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 34653190 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis by confocal laser scanning microscopy of the MDPB bactericidal effect on S. mutans biofilm CLSM analysis of MDPB bactericidal effect on biofilm.J Appl Oral Sci. 2012 Sep-Oct;20(5):568-75. doi: 10.1590/s1678-77572012000500013. J Appl Oral Sci. 2012. PMID: 23138745 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Brogden, K. A. 2005. Antimicrobial peptides: pore formers or metabolic inhibitors in bacteria? Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 3:238-250. - PubMed
-
- Burne, R. A. 1998. Oral streptococci…products of their environment. J. Dent. Res. 77:445-452. - PubMed
-
- Chen, X., H. Tang, M. A. Even, J. Wang, G. N. Tew, and Z. Chen. 2006. Observing a molecular knife at work. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 128:2711-2714. - PubMed
-
- Cole, A. M., P. Weis, and G. Diamond. 1997. Isolation and characterization of pleurocidin, an antimicrobial peptide in the skin secretions of winter flounder. J. Biol. Chem. 272:12008-12013. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

