ASY1 mediates AtDMC1-dependent interhomolog recombination during meiosis in Arabidopsis
- PMID: 17785529
- PMCID: PMC1950860
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.439007
ASY1 mediates AtDMC1-dependent interhomolog recombination during meiosis in Arabidopsis
Abstract
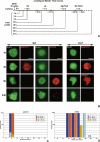
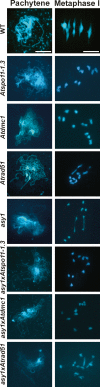
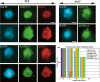
ASY1 is an Arabidopsis protein required for synapsis and crossover formation during meiosis. The chronology of meiotic recombination has been investigated in wild type and an asy1 mutant. We observe a delay between the appearance of chromatin-associated AtSPO11-1 foci and DNA double-strand break (DSB) formation, which occurs contemporaneously with chromosome axis formation and transition of ASY1 from chromatin-associated foci to a linear axis-associated signal. DSBs are formed independently of ASY1 in an AtSPO11-1-dependent manner. They are partially restored in Atspo11-1-3 using cisplatin, but their control appears abnormal. Axis morphogenesis is independent of ASY1, but axis structure may be compromised in asy1. Localization of the strand exchange proteins AtRAD51 and AtDMC1 to the chromatin occurs asynchronously shortly after DSB formation, with AtDMC1 localizing in advance of AtRAD51. In wild-type nuclei, both recombinases form numerous foci that persist for approximately 12 h before gradually decreasing in number. In asy1, initial localization of AtDMC1 is normal, but declines abruptly such that interhomolog recombination is severely compromised. Limited ASY1-independent, DMC1-dependent interhomolog recombination remains, but appears restricted to subtelomeric sequences where the homologs are fortuitously in proximity. Thus, ASY1 plays a key role in coordinating the activity of the RecA homologs to create a bias in favor of interhomolog recombination.
Figures



References
-
- Allers T., Lichten M., Lichten M. Differential timing and control of noncrossover and crossover recombination during meiosis. Cell. 2001;106:47–57. - PubMed
-
- Alonso J.M., Stepanova A.N., Leisse T.J., Kim C.J., Chen H., Shinn P., Stevenson D.K., Zimmerman J., Barajas P., Cheuk R., Stepanova A.N., Leisse T.J., Kim C.J., Chen H., Shinn P., Stevenson D.K., Zimmerman J., Barajas P., Cheuk R., Leisse T.J., Kim C.J., Chen H., Shinn P., Stevenson D.K., Zimmerman J., Barajas P., Cheuk R., Kim C.J., Chen H., Shinn P., Stevenson D.K., Zimmerman J., Barajas P., Cheuk R., Chen H., Shinn P., Stevenson D.K., Zimmerman J., Barajas P., Cheuk R., Shinn P., Stevenson D.K., Zimmerman J., Barajas P., Cheuk R., Stevenson D.K., Zimmerman J., Barajas P., Cheuk R., Zimmerman J., Barajas P., Cheuk R., Barajas P., Cheuk R., Cheuk R., et al. Genome-wide insertional mutagenesis of Arabidopsis thaliana. Science. 2003;301:653–657. - PubMed
-
- Armstrong S.J., Franklin F.C.H., Jones G.H., Franklin F.C.H., Jones G.H., Jones G.H. Nucleolus-associated telomere clustering and pairing precede meiotic chromosome synapsis in Arabidopsis thaliana. J. Cell Sci. 2001;114:4207–4217. - PubMed
-
- Armstrong S.J., Caryl A.P., Jones G.H., Franklin F.C.H., Caryl A.P., Jones G.H., Franklin F.C.H., Jones G.H., Franklin F.C.H., Franklin F.C.H. Asy1, a protein required for meiotic chromosome synapsis, localizes to axis-associated chromatin in Arabidopsis and Brassica. J. Cell Sci. 2002;115:3645–3655. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
