A systems biology approach for pathway level analysis
- PMID: 17785539
- PMCID: PMC1987343
- DOI: 10.1101/gr.6202607
A systems biology approach for pathway level analysis
Abstract
A common challenge in the analysis of genomics data is trying to understand the underlying phenomenon in the context of all complex interactions taking place on various signaling pathways. A statistical approach using various models is universally used to identify the most relevant pathways in a given experiment. Here, we show that the existing pathway analysis methods fail to take into consideration important biological aspects and may provide incorrect results in certain situations. By using a systems biology approach, we developed an impact analysis that includes the classical statistics but also considers other crucial factors such as the magnitude of each gene's expression change, their type and position in the given pathways, their interactions, etc. The impact analysis is an attempt to a deeper level of statistical analysis, informed by more pathway-specific biology than the existing techniques. On several illustrative data sets, the classical analysis produces both false positives and false negatives, while the impact analysis provides biologically meaningful results. This analysis method has been implemented as a Web-based tool, Pathway-Express, freely available as part of the Onto-Tools (http://vortex.cs.wayne.edu).
Figures
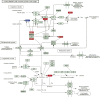

References
-
- Beer D.G., Kardia S.L., Huang C.-C., Giordano T.J., Levin A.M., Misek D.E., Lin L., Chen G., Gharib T.G., Thomas D.G., Kardia S.L., Huang C.-C., Giordano T.J., Levin A.M., Misek D.E., Lin L., Chen G., Gharib T.G., Thomas D.G., Huang C.-C., Giordano T.J., Levin A.M., Misek D.E., Lin L., Chen G., Gharib T.G., Thomas D.G., Giordano T.J., Levin A.M., Misek D.E., Lin L., Chen G., Gharib T.G., Thomas D.G., Levin A.M., Misek D.E., Lin L., Chen G., Gharib T.G., Thomas D.G., Misek D.E., Lin L., Chen G., Gharib T.G., Thomas D.G., Lin L., Chen G., Gharib T.G., Thomas D.G., Chen G., Gharib T.G., Thomas D.G., Gharib T.G., Thomas D.G., Thomas D.G., et al. Gene-expression profiles predict survival of patients with lung adenocarcinoma. Nat. Med. 2002;8:816–824. - PubMed
-
- Beviglia L., Golubovskaya V., Xu L., Yang X., Craven R.J., Cance W.G., Golubovskaya V., Xu L., Yang X., Craven R.J., Cance W.G., Xu L., Yang X., Craven R.J., Cance W.G., Yang X., Craven R.J., Cance W.G., Craven R.J., Cance W.G., Cance W.G. Focal adhesion kinase N-terminus in breast carcinoma cells induces rounding, detachment and apoptosis. Biochem. J. 2003;373:201–210. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Canales R.D., Luo Y., Willey J.C., Austermiller B., Barbacioru C.C., Boysen C., Hunkapiller K., Jensen R.V., Knight C.R., Lee K.Y., Luo Y., Willey J.C., Austermiller B., Barbacioru C.C., Boysen C., Hunkapiller K., Jensen R.V., Knight C.R., Lee K.Y., Willey J.C., Austermiller B., Barbacioru C.C., Boysen C., Hunkapiller K., Jensen R.V., Knight C.R., Lee K.Y., Austermiller B., Barbacioru C.C., Boysen C., Hunkapiller K., Jensen R.V., Knight C.R., Lee K.Y., Barbacioru C.C., Boysen C., Hunkapiller K., Jensen R.V., Knight C.R., Lee K.Y., Boysen C., Hunkapiller K., Jensen R.V., Knight C.R., Lee K.Y., Hunkapiller K., Jensen R.V., Knight C.R., Lee K.Y., Jensen R.V., Knight C.R., Lee K.Y., Knight C.R., Lee K.Y., Lee K.Y., et al. Evaluation of DNA microarray results with quantitative gene expression platforms. Nat. Biotechnol. 2006;24:1115–1122. - PubMed
-
- Chen Z., Gibson T.B., Robinson F., Silvestro L., Pearson G., Xu B., Wright A., Vanderbilt C., Cobb M.H., Gibson T.B., Robinson F., Silvestro L., Pearson G., Xu B., Wright A., Vanderbilt C., Cobb M.H., Robinson F., Silvestro L., Pearson G., Xu B., Wright A., Vanderbilt C., Cobb M.H., Silvestro L., Pearson G., Xu B., Wright A., Vanderbilt C., Cobb M.H., Pearson G., Xu B., Wright A., Vanderbilt C., Cobb M.H., Xu B., Wright A., Vanderbilt C., Cobb M.H., Wright A., Vanderbilt C., Cobb M.H., Vanderbilt C., Cobb M.H., Cobb M.H. MAP kinases. Chem. Rev. 2001;101:2449–2476. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R21 CA100740/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 2P30 CA022453-24/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 5R21EB00090-03/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- 1R21CA100740-01/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R21 EB000990/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA117478/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- S10 RR017857/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS045207/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA022453/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 1U01CA117478-01/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HG003491/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- 1S10 RR017857-01/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- 1R01NS045207-01/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- 1R01HG003491-01A1/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
