MicroRNAs: powerful new regulators of heart disease and provocative therapeutic targets
- PMID: 17786230
- PMCID: PMC1952642
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI33099
MicroRNAs: powerful new regulators of heart disease and provocative therapeutic targets
Abstract
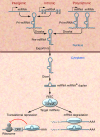
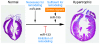
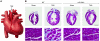
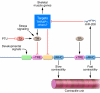
MicroRNAs act as negative regulators of gene expression by inhibiting the translation or promoting the degradation of target mRNAs. Recent studies have revealed key roles of microRNAs as regulators of the growth, development, function, and stress responsiveness of the heart, providing glimpses of undiscovered regulatory mechanisms and potential therapeutic targets for the treatment of heart disease.
Figures

References
-
- Hoffman J.I. Incidence of congenital heart disease: II. Prenatal incidence. Pediatr. Cardiol. 1995;16:155–165. - PubMed
-
- Rosamond W., et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics--2007 update: a report from the American Heart Association Statistics Committee and Stroke Statistics Subcommittee. Circulation. 2007;115:e69–e171. - PubMed
-
- Yang B., et al. The muscle-specific microRNA miR-1 regulates cardiac arrhythmogenic potential by targeting GJA1 and KCNJ2. Nat. Med. 2007;13:486–491. - PubMed
-
- Zhao Y., et al. Dysregulation of cardiogenesis, cardiac conduction, and cell cycle in mice lacking miRNA-1-2. Cell. 2007;129:303–317. - PubMed
-
- van Rooij E., et al. Control of stress-dependent cardiac growth and gene expression by a microRNA. Science. 2007;316:575–579. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

