Beta-arrestin-mediated beta1-adrenergic receptor transactivation of the EGFR confers cardioprotection
- PMID: 17786238
- PMCID: PMC1952636
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI31901
Beta-arrestin-mediated beta1-adrenergic receptor transactivation of the EGFR confers cardioprotection
Abstract
Deleterious effects on the heart from chronic stimulation of beta-adrenergic receptors (betaARs), members of the 7 transmembrane receptor family, have classically been shown to result from Gs-dependent adenylyl cyclase activation. Here, we identify a new signaling mechanism using both in vitro and in vivo systems whereby beta-arrestins mediate beta1AR signaling to the EGFR. This beta-arrestin-dependent transactivation of the EGFR, which is independent of G protein activation, requires the G protein-coupled receptor kinases 5 and 6. In mice undergoing chronic sympathetic stimulation, this novel signaling pathway is shown to promote activation of cardioprotective pathways that counteract the effects of catecholamine toxicity. These findings suggest that drugs that act as classical antagonists for G protein signaling, but also stimulate signaling via beta-arrestin-mediated cytoprotective pathways, would represent a novel class of agents that could be developed for multiple members of the 7 transmembrane receptor family.
Figures
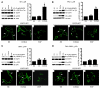
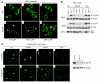

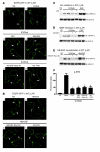
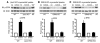
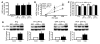

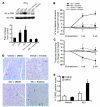
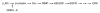
Comment in
-
Alternative signaling: cardiomyocyte beta1-adrenergic receptors signal through EGFRs.J Clin Invest. 2007 Sep;117(9):2396-8. doi: 10.1172/JCI33135. J Clin Invest. 2007. PMID: 17786237 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rockman H.A., Koch W.J., Lefkowitz R.J. Seven-transmembrane-spanning receptors and heart function. Nature. 2002;415:206–212. - PubMed
-
- Koch W.J., Lefkowitz R.J., Rockman H.A. Functional consequences of altering myocardial adrenergic receptor signaling. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2000;62:237–260. - PubMed
-
- Lefkowitz R.J. G protein-coupled receptors. III. New roles for receptor kinases and beta-arrestins in receptor signaling and desensitization. . J. Biol. Chem. 1998;273:18677–18680. - PubMed
-
- Maudsley S., et al. The beta(2)-adrenergic receptor mediates extracellular signal-regulated kinase activation via assembly of a multi-receptor complex with the epidermal growth factor receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 2000;275:9572–9580. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

