Regulation of the rat glutathione S-transferase A2 gene by glucocorticoids: crosstalk through C/EBPs
- PMID: 17786629
- PMCID: PMC2423428
- DOI: 10.1080/03602530701511216
Regulation of the rat glutathione S-transferase A2 gene by glucocorticoids: crosstalk through C/EBPs
Abstract
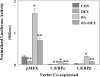
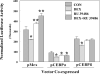
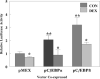
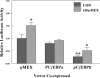
Regulation of the rat glutathione S-transferase A2 (GSTA2) gene by glucocorticoids is biphasic in its concentration dependence to glucocorticoids, with concentrations of 10-100 nM repressing gene activity (GR-dependent), and concentrations above 1 microM increasing transactivation (PXR-dependent) in adult rat hepatocytes or transient transfection assays. Over-expression of either C/EBP alpha or beta negatively regulates basal and inducible expression of a 1.65 Kb GSTA2 luciferase reporter, and synergizes the response to glucocorticoids (GC). C/EBP responsive elements have been identified in the GSTA2 5'-flanking sequence, associated with the palindrominic Glucocorticoid Responsive Element (GRE), the Ah receptor response elements, and the antioxidant response element. In reporters lacking the palindromic GRE, negative regulation by GC is observed only when C/EBP alpha is co-expressed. Co-transfection of C/EBP alpha/beta induced gene expression of the GSTA2 XRE reporter, but negatively regulated the GSTA2 ARE-reporter. In contrast, the ARE from the rat NAD(P)H quinone oxidoreductase gene was induced by co-transfection of C/EBPs, but was still negatively regulated by GC. PXR-induction of the GSTA2 reporter was partially ablated by co-transfection of C/EBP alpha and enhanced by co-transfection of C/EBPbeta. We conclude that C/EBP alpha and beta are involved in GC-dependent repression of GSTA2 gene expression and ARE sequences that bind C/EBPs appears to be critical for these responses.
Figures


References
-
- Abramovitz M, Listowsky I. Developmental regulation of glutathione S-transferases. Xenobiotica. 1988;18:1249–1254. - PubMed
-
- Birkenmeier EH, Gwynn B, Howard S, Jerry J, Gordon JI, Landschulz WH, McKnight SL. Tissue-specific expression, developmental regulation, and genetic mapping of the gene encoding CCAAT/enhancer binding protein. Genes Dev. 1989;3:1146–1156. - PubMed
-
- Chen Y-H, Ramos KS. A CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein site within the antioxidant/electrophile response element along with CREB-binding protein participate in the negative regulation of rat GST-Ya gene in vascular smooth muscle cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2000;275:27366–27376. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
