Docking of the proteasomal ATPases' carboxyl termini in the 20S proteasome's alpha ring opens the gate for substrate entry
- PMID: 17803938
- PMCID: PMC2083707
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2007.06.033
Docking of the proteasomal ATPases' carboxyl termini in the 20S proteasome's alpha ring opens the gate for substrate entry
Abstract
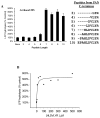
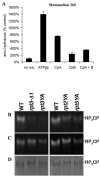
The 20S proteasome functions in protein degradation in eukaryotes together with the 19S ATPases or in archaea with the homologous PAN ATPase complex. These ATPases contain a conserved C-terminal hydrophobic-tyrosine-X motif (HbYX). We show that these residues are essential for PAN to associate with the 20S and open its gated channel for substrate entry. Upon ATP binding, these C-terminal residues bind to pockets between the 20S's alpha subunits. Seven-residue or longer peptides from PAN's C terminus containing the HbYX motif also bind to these sites and induce gate opening in the 20S. Gate opening could be induced by C-terminal peptides from the 19S ATPase subunits, Rpt2, and Rpt5, but not by ones from PA28/26, which lack the HbYX motif and cause gate opening by distinct mechanisms. C-terminal residues in the 19S ATPases were also shown to be critical for gating and stability of 26S proteasomes. Thus, the C termini of the proteasomal ATPases function like a "key in a lock" to induce gate opening and allow substrate entry.
Figures





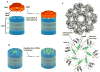
Comment in
-
Unlocking the proteasome door.Mol Cell. 2007 Sep 21;27(6):865-7. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2007.09.001. Mol Cell. 2007. PMID: 17889660
References
-
- Adams J. Proteasome inhibitors in cancer therapy. Totowa, N.J: Humana Press; 2004.
-
- Ames BN. Assay of inorganic Phosphate, Total Phosphate and Phosphatases. Methods in Enzymology. 1966;8:115–118.
-
- Benaroudj N, Smith DM, Goldberg AL. What the archaeal PAN-proteasome complex and bacterial ATPdependent proteases can teach us about the 26S proteasome. Vol. 2. The Ubiquitin-Proteasome System; Wiley-VCH: 2005.
-
- Benaroudj N, Zwickl P, Seemuller E, Baumeister W, Goldberg AL. ATP hydrolysis by the proteasome regulatory complex PAN serves multiple functions in protein degradation. Mol Cell. 2003;11:69–78. - PubMed
-
- Bochtler M, Hartmann C, Song HK, Bourenkov GP, Bartunik HD, Huber R. The structures of HsIU and the ATP-dependent protease HsIU-HsIV. Nature. 2000;403:800–805. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

