Hippocampal CA1 place cells encode intended destination on a maze with multiple choice points
- PMID: 17804637
- PMCID: PMC6672960
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2011-07.2007
Hippocampal CA1 place cells encode intended destination on a maze with multiple choice points
Abstract
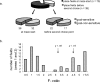
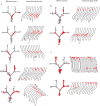
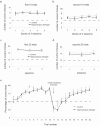
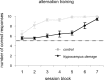
The hippocampus encodes both spatial and nonspatial aspects of a rat's ongoing behavior at the single-cell level. In this study, we examined the encoding of intended destination by hippocampal (CA1) place cells during performance of a serial reversal task on a double Y-maze. On the maze, rats had to make two choices to access one of four possible goal locations, two of which contained reward. Reward locations were kept constant within blocks of 10 trials but changed between blocks, and the session of each day comprised three or more trial blocks. A disproportionate number of place fields were observed in the start box and beginning stem of the maze, relative to other locations on the maze. Forty-six percent of these place fields had different firing rates on journeys to different goal boxes. Another group of cells had place fields before the second choice point, and, of these, 44% differentiated between journeys to specific goal boxes. In a second experiment, we observed that rats with hippocampal damage made significantly more errors than control rats on the Y-maze when reward locations were reversed. Together, these results suggest that, at the start of the maze, the hippocampus encodes both current location and the intended destination of the rat, and this encoding is necessary for the flexible response to changes in reinforcement contingencies.
Figures
References
-
- Ainge JA, Heron-Maxwell C, Theofilas P, Wright P, de Hoz L, Wood ER. The role of the hippocampus in object recognition in rats: examination of the influence of task parameters and lesion size. Behav Brain Res. 2006;167:183–195. - PubMed
-
- Ainge JA, van der Meer M, Langston RF, Wood ER. Exploring the role of context dependent hippocampal activity in spatial alternation behaviour. Hippocampus. 2007 in press. - PubMed
-
- Bahar AS, Shapiro ML. Reorganised prospective and retrospective hippocampal memory coding after switching the start and goal of a journey. Soc Neurosci Abstr. 2006;32:68–21.
-
- Barnes TD, Kubota Y, Hu D, Jin DZ, Graybiel AM. Activity of striatal neurons reflects dynamic encoding and recoding of procedural memories. Nature. 2005;437:1158–1161. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
