Genetic diversity of paired middle-ear and pharyngeal nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae isolates from children with acute otitis media
- PMID: 17804648
- PMCID: PMC2168485
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.00964-07
Genetic diversity of paired middle-ear and pharyngeal nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae isolates from children with acute otitis media
Abstract
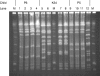
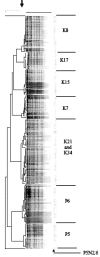
Pulsed-field gel electrophoresis was used to determine genetic diversities of multiple nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae isolates from throat and ear specimens of eight children with otitis media. From five children, all ear and throat isolates were identical. The bacterial populations in these specimens showed less diversity than populations in throat isolates of healthy children.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Identification of new genetic regions more prevalent in nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae otitis media strains than in throat strains.J Clin Microbiol. 2006 Dec;44(12):4316-25. doi: 10.1128/JCM.01331-06. Epub 2006 Sep 27. J Clin Microbiol. 2006. PMID: 17005745 Free PMC article.
-
Genotyping of Streptococcus pneumoniae and Haemophilus influenzae isolated from paired middle ear fluid and nasopharynx by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis.ORL J Otorhinolaryngol Relat Spec. 2004;66(5):233-40. doi: 10.1159/000081119. ORL J Otorhinolaryngol Relat Spec. 2004. PMID: 15583436
-
Risk factors for otitis media and carriage of multiple strains of Haemophilus influenzae and Streptococcus pneumoniae.Emerg Infect Dis. 2000 Nov-Dec;6(6):622-30. doi: 10.3201/eid0606.000611. Emerg Infect Dis. 2000. PMID: 11076721 Free PMC article.
-
Otitis media: etiology and diagnosis.Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1994 Jan;13(1 Suppl 1):S23-6; discussion S50-4. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1994. PMID: 8159511 Review. No abstract available.
-
Nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae as a pathogen in children.Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2009 Jan;28(1):43-8. doi: 10.1097/INF.0b013e318184dba2. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2009. PMID: 19057458 Review.
Cited by
-
Phase variation and host immunity against high molecular weight (HMW) adhesins shape population dynamics of nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae within human hosts.J Theor Biol. 2014 Aug 21;355:208-18. doi: 10.1016/j.jtbi.2014.04.010. Epub 2014 Apr 18. J Theor Biol. 2014. PMID: 24747580 Free PMC article.
-
Antagonistic Pleiotropy in the Bifunctional Surface Protein FadL (OmpP1) during Adaptation of Haemophilus influenzae to Chronic Lung Infection Associated with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease.mBio. 2018 Sep 25;9(5):e01176-18. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01176-18. mBio. 2018. PMID: 30254117 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence of Haemophilus influenzae type b genetic islands among clinical and commensal H. influenzae and H. haemolyticus isolates.J Clin Microbiol. 2010 Jul;48(7):2565-8. doi: 10.1128/JCM.02453-09. Epub 2010 May 12. J Clin Microbiol. 2010. PMID: 20463164 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aniansson, G., B. Alm, B. Andersson, P. Larsson, O. Nylen, H. Peterson, P. Ringer, M. Svanborg, and C. Svanborg. 1992. Nasopharyngeal colonization during the first year of life. J. Infect. Dis. 165:S38-S42. - PubMed
-
- Barbosa-Cesnik, C., R. S. Farjo, M. Patel, J. Gilsdorf, S. I. McCoy, M. M. Pettigrew, C. Marrs, and B. Foxman. 2006. Predictors for Haemophilus influenzae colonization, antibiotic resistance, and for sharing an identical isolate among children attending 16 licensed day-care centers in Michigan. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 25:219-223. - PubMed
-
- Casselbrant, M. L., E. M. Mandel, P. A. Fall, H. E. Rockette, M. Kurs-Lasky, C. D. Bluestone, and R. E. Ferrell. 1999. The heritability of otitis media: a twin and triplet study. JAMA 282:2125-2130. - PubMed
-
- Eskola, J., and T. Kilpi. 2000. Potential of bacterial vaccines in the prevention of acute otitis media. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. 19:72-80. - PubMed
-
- Farjo, R. S., B. Foxman, M. J. Patel, L. Zhang, M. M. Pettigrew, S. I. McCoy, C. F. Marrs, and J. R. Gilsdorf. 2004. Diversity and sharing of Haemophilus influenzae strains colonizing healthy children attending day-care centers. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 23:41-46. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

