Ribosome biogenesis and the translation process in Escherichia coli
- PMID: 17804668
- PMCID: PMC2168646
- DOI: 10.1128/MMBR.00013-07
Ribosome biogenesis and the translation process in Escherichia coli
Abstract
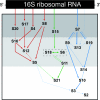
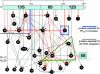
Translation, the decoding of mRNA into protein, is the third and final element of the central dogma. The ribosome, a nucleoprotein particle, is responsible and essential for this process. The bacterial ribosome consists of three rRNA molecules and approximately 55 proteins, components that are put together in an intricate and tightly regulated way. When finally matured, the quality of the particle, as well as the amount of active ribosomes, must be checked. The focus of this review is ribosome biogenesis in Escherichia coli and its cross-talk with the ongoing protein synthesis. We discuss how the ribosomal components are produced and how their synthesis is regulated according to growth rate and the nutritional contents of the medium. We also present the many accessory factors important for the correct assembly process, the list of which has grown substantially during the last few years, even though the precise mechanisms and roles of most of the proteins are not understood.
Figures


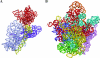
References
-
- Adilakshimi, T., P. Ramaswamy, and S. A. Woodson. 2005. Protein-independent folding pathway of the 16S rRNA 5′ domain. J. Mol. Biol. 351:508-519. - PubMed
-
- Agrawal, R. K., R. K. Lata, and J. Frank. 1999. Conformational variability in Escherichia coli 70S ribosome as revealed by 3D cryo-electron tomography. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 31:243-254. - PubMed
-
- Alix, J. H., D. Hayes, and K. N. Nierhaus. 1979. Properties of ribosomes and RNA synthesized by Escherichia coli grown in the presence of ethionine. V. Methylation dependence of the assembly of E. coli 50S ribosomal subunits. J. Mol. Biol. 127:375-395. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

