Genetic screening reveals an essential role of p27kip1 in restriction of breast cancer progression
- PMID: 17804714
- PMCID: PMC2412956
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-0083
Genetic screening reveals an essential role of p27kip1 in restriction of breast cancer progression
Abstract
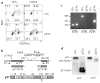
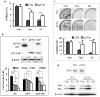
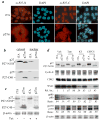
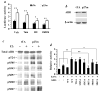
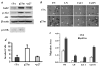
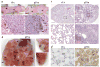
The genetic changes and mechanisms underlying the progression of estrogen-dependent breast cancers to estrogen-independent, antiestrogen-resistant, and metastatic breast cancers are unclear despite being a major problem in endocrine therapy. To identify genes responsible for this progression, we carried out a genetic screening by an enhanced retroviral mutagen (ERM)-mediated random mutagenesis in the estrogen-dependent T47D breast cancer cells. We found that T47D cells contain only one p27kip1 (p27) allele coding for the p27 cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK) inhibitor. An ERM insertion into the p27 locus of T47D cells disrupted the p27 gene and created estrogen-independent and antiestrogen-resistant breast cancer cells that still maintained functional estrogen receptors. Disruption of p27 in T47D cells resulted in several changes, and most of these changes could be rescued by p27 restoration. First, CDK2 activity was increased in the absence of estrogen or in the presence of estrogen antagonists tamoxifen or ICI 182780; second, amplified in breast cancer 1 (AIB1), a cancer overexpressed transcriptional coactivator, was hyperphosphorylated, which made AIB1 a better coactivator for E2F1; and third, growth factor receptor binding protein 2-associated binder 2 (Gab2) and Akt activity were increased following E2F1 overactivation, leading to a significant enhancement of cell migration and invasion. Furthermore, the p27-deficient cells, but not T47D control cells, developed lung metastasis in an ovarian hormone-independent manner when they were i.v. injected into nude mice. In sum, loss of p27 activated AIB1, E2F1, Gab2, and Akt; increased cell migration and invasion; caused antiestrogen insensitivity; and promoted metastasis of breast cancer cells. These findings suggest that p27 plays an essential role in restriction of breast cancer progression.
Figures
References
-
- Doisneau-Sixou SF, Sergio CM, Carroll JS, Hui R, Musgrove EA, Sutherland RL. Estrogen and antiestrogen regulation of cell cycle progression in breast cancer cells. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2003;10:179–86. - PubMed
-
- Foster JS, Fernando RI, Ishida N, Nakayama KI, Wimalasena J. Estrogens down-regulate p27Kip1 in breast cancer cells through Skp2 and through nuclear export mediated by the ERK pathway. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:41355–66. - PubMed
-
- Jordan VC. Third annual William L. McGuire Memorial Lecture “Studies on the estrogen receptor in breast cancer”--20 years as a target for the treatment and prevention of cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 1995;36:267–85. - PubMed
-
- Schiff R, Massarweh S, Shou J, Osborne CK. Breast cancer endocrine resistance: how growth factor signaling and estrogen receptor coregulators modulate response. Clin Cancer Res. 2003;9(Pt 2):447S–54S. - PubMed
-
- Brodie A. Aromatase inhibitor development and hormone therapy: a perspective. Semin Oncol. 2003;30(Suppl 14):12–22. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

