Astrocytes regulate GluR2 expression in motor neurons and their vulnerability to excitotoxicity
- PMID: 17804792
- PMCID: PMC1976195
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0705046104
Astrocytes regulate GluR2 expression in motor neurons and their vulnerability to excitotoxicity
Abstract
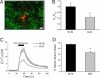
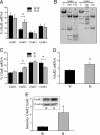
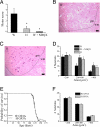
Influx of Ca(2+) ions through alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methylisoxazole-4-propionic acid (AMPA) receptors contributes to neuronal damage in stroke, epilepsy, and neurodegenerative disorders such as ALS. The Ca(2+) permeability of AMPA receptors is largely determined by the glutamate receptor 2 (GluR2) subunit, receptors lacking GluR2 being permeable to Ca(2+) ions. We identified a difference in GluR2 expression in motor neurons from two rat strains, resulting in a difference in vulnerability to AMPA receptor-mediated excitotoxicity both in vitro and in vivo. Astrocytes from the ventral spinal cord were found to mediate this difference in GluR2 expression in motor neurons. The presence of ALS-causing mutant superoxide dismutase 1 in astrocytes abolished their GluR2-regulating capacity and thus affected motor neuron vulnerability to AMPA receptor-mediated excitotoxicity. These results reveal a mechanism through which astrocytes influence neuronal functioning in health and disease.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
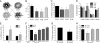
References
-
- Lipton SA, Rosenberg PA. N Engl J Med. 1994;330:613–622. - PubMed
-
- Van Den Bosch L, Van Damme P, Bogaert E, Robberecht W. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2006;1762:1068–1082. - PubMed
-
- Hollmann M, Hartley M, Heinemann S. Science. 1991;252:851–853. - PubMed
-
- Sommer B, Kohler M, Sprengel R, Seeburg PH. Cell. 1991;67:11–19. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

