Recent transcontinental sweep of Toxoplasma gondii driven by a single monomorphic chromosome
- PMID: 17804804
- PMCID: PMC1965483
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0702356104
Recent transcontinental sweep of Toxoplasma gondii driven by a single monomorphic chromosome
Abstract
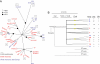
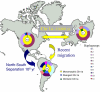
Toxoplasma gondii is a highly prevalent protozoan parasite that infects a wide range of animals and threatens human health by contaminating food and water. A markedly limited number of clonal parasite lineages have been recognized as predominating in North American and European populations, whereas strains from South America are comparatively diverse. Here, we show that strains from North America and Europe share distinct genetic polymorphisms that are mutually exclusive from polymorphisms in strains from the south. A striking exception to this geographic segregation is a monomorphic version of one chromosome (Chr1a) that characterizes virtually all northern and many southern isolates. Using a combination of molecular phylogenetic and phenotypic analyses, we conclude that northern and southern parasite populations diverged from a common ancestor in isolation over a period of approximately 10(6) yr, and that the monomorphic Chr1a has swept each population within the past 10,000 years. Like its definitive feline hosts, T. gondii may have entered South America and diversified there after reestablishment of the Panamanian land bridge. Since then, recombination has been an infrequent but important force in generating new T. gondii genotypes. Genes unique to a monomorphic version of a single parasite chromosome may have facilitated a recent population sweep of a limited number of highly successful T. gondii lineages.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Joynson DH, Wreghitt TJ. Toxoplasmosis: A Comprehensive Clinical Guide. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge Univ Press; 2001.
-
- Howe DK, Sibley LD. J Infect Dis. 1995;172:1561–1566. - PubMed
-
- Ajzenberg D, Bañuls AL, Su C, Dumètre A, Demar M, Carme B, Dardé ML. Intl J Parasitol. 2004;34:1185–1196. - PubMed
-
- Sibley LD, Boothroyd JC. Nature. 1992;359:82–85. - PubMed
-
- Grigg ME, Bonnefoy S, Hehl AB, Suzuki Y, Boothroyd JC. Science. 2001;294:161–165. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

