ARL4D recruits cytohesin-2/ARNO to modulate actin remodeling
- PMID: 17804820
- PMCID: PMC2043562
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e07-02-0149
ARL4D recruits cytohesin-2/ARNO to modulate actin remodeling
Abstract
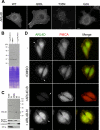
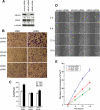
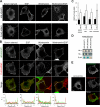
ARL4D is a developmentally regulated member of the ADP-ribosylation factor/ARF-like protein (ARF/ARL) family of Ras-related GTPases. Although the primary structure of ARL4D is very similar to that of other ARF/ARL molecules, its function remains unclear. Cytohesin-2/ARF nucleotide-binding-site opener (ARNO) is a guanine nucleotide-exchange factor (GEF) for ARF, and, at the plasma membrane, it can activate ARF6 to regulate actin reorganization and membrane ruffling. We show here that ARL4D interacts with the C-terminal pleckstrin homology (PH) and polybasic c domains of cytohesin-2/ARNO in a GTP-dependent manner. Localization of ARL4D at the plasma membrane is GTP- and N-terminal myristoylation-dependent. ARL4D(Q80L), a putative active form of ARL4D, induced accumulation of cytohesin-2/ARNO at the plasma membrane. Consistent with a known action of cytohesin-2/ARNO, ARL4D(Q80L) increased GTP-bound ARF6 and induced disassembly of actin stress fibers. Expression of inactive cytohesin-2/ARNO(E156K) or small interfering RNA knockdown of cytohesin-2/ARNO blocked ARL4D-mediated disassembly of actin stress fibers. Similar to the results with cytohesin-2/ARNO or ARF6, reduction of ARL4D suppressed cell migration activity. Furthermore, ARL4D-induced translocation of cytohesin-2/ARNO did not require phosphoinositide 3-kinase activation. Together, these data demonstrate that ARL4D acts as a novel upstream regulator of cytohesin-2/ARNO to promote ARF6 activation and modulate actin remodeling.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Active Arf6 recruits ARNO/cytohesin GEFs to the PM by binding their PH domains.Mol Biol Cell. 2007 Jun;18(6):2244-53. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e06-11-0998. Epub 2007 Apr 4. Mol Biol Cell. 2007. PMID: 17409355 Free PMC article.
-
The N-terminal coiled-coil domain of the cytohesin/ARNO family of guanine nucleotide exchange factors interacts with Galphaq.Mol Cell Biochem. 2007 Dec;306(1-2):141-52. doi: 10.1007/s11010-007-9564-9. Epub 2007 Sep 6. Mol Cell Biochem. 2007. PMID: 17846866
-
The Arl4 family of small G proteins can recruit the cytohesin Arf6 exchange factors to the plasma membrane.Curr Biol. 2007 Apr 17;17(8):711-6. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2007.03.007. Epub 2007 Mar 29. Curr Biol. 2007. PMID: 17398095
-
Potential regulation of ADP-ribosylation factor 6 signalling by phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate.Biochem Soc Trans. 1999 Aug;27(4):683-9. doi: 10.1042/bst0270683. Biochem Soc Trans. 1999. PMID: 10917667 Review.
-
The role of ADP-ribosylation factor and SAR1 in vesicular trafficking in plants.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2004 Jul 1;1664(1):9-30. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2004.04.005. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2004. PMID: 15238254 Review.
Cited by
-
An update on genetically encoded lipid biosensors.Mol Biol Cell. 2022 May 1;33(5):tp2. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E21-07-0363. Mol Biol Cell. 2022. PMID: 35420888 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphorylation of Arl4A/D promotes their binding by the HYPK chaperone for their stable recruitment to the plasma membrane.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022 Jul 26;119(30):e2207414119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2207414119. Epub 2022 Jul 20. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022. PMID: 35857868 Free PMC article.
-
Structural basis for membrane recruitment and allosteric activation of cytohesin family Arf GTPase exchange factors.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013 Aug 27;110(35):14213-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1301883110. Epub 2013 Aug 12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013. PMID: 23940353 Free PMC article.
-
Polyphosphoinositide binding domains: Key to inositol lipid biology.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015 Jun;1851(6):746-58. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2015.02.013. Epub 2015 Feb 27. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015. PMID: 25732852 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A novel functional gene selection method provides a systematic view of cell migration.Cell Adh Migr. 2010 Apr-Jun;4(2):207-10. doi: 10.4161/cam.4.2.11073. Epub 2010 Apr 22. Cell Adh Migr. 2010. PMID: 20215876 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Balch W. E., Kahn R. A., Schwaninger R. ADP-ribosylation factor is required for vesicular trafficking between the endoplasmic reticulum and the cis-Golgi compartment. J. Biol. Chem. 1992;267:13053–13061. - PubMed
-
- Balla T. Inositol-lipid binding motifs: signal integrators through protein-lipid and protein-protein interactions. J. Cell Sci. 2005;118:2093–2104. - PubMed
-
- Barrios-Rodiles M., et al. High-throughput mapping of a dynamic signaling network in mammalian cells. Science. 2005;307:1621–1625. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

