ARL4D recruits cytohesin-2/ARNO to modulate actin remodeling
- PMID: 17804820
- PMCID: PMC2043562
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e07-02-0149
ARL4D recruits cytohesin-2/ARNO to modulate actin remodeling
Abstract
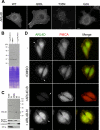
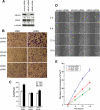
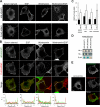
ARL4D is a developmentally regulated member of the ADP-ribosylation factor/ARF-like protein (ARF/ARL) family of Ras-related GTPases. Although the primary structure of ARL4D is very similar to that of other ARF/ARL molecules, its function remains unclear. Cytohesin-2/ARF nucleotide-binding-site opener (ARNO) is a guanine nucleotide-exchange factor (GEF) for ARF, and, at the plasma membrane, it can activate ARF6 to regulate actin reorganization and membrane ruffling. We show here that ARL4D interacts with the C-terminal pleckstrin homology (PH) and polybasic c domains of cytohesin-2/ARNO in a GTP-dependent manner. Localization of ARL4D at the plasma membrane is GTP- and N-terminal myristoylation-dependent. ARL4D(Q80L), a putative active form of ARL4D, induced accumulation of cytohesin-2/ARNO at the plasma membrane. Consistent with a known action of cytohesin-2/ARNO, ARL4D(Q80L) increased GTP-bound ARF6 and induced disassembly of actin stress fibers. Expression of inactive cytohesin-2/ARNO(E156K) or small interfering RNA knockdown of cytohesin-2/ARNO blocked ARL4D-mediated disassembly of actin stress fibers. Similar to the results with cytohesin-2/ARNO or ARF6, reduction of ARL4D suppressed cell migration activity. Furthermore, ARL4D-induced translocation of cytohesin-2/ARNO did not require phosphoinositide 3-kinase activation. Together, these data demonstrate that ARL4D acts as a novel upstream regulator of cytohesin-2/ARNO to promote ARF6 activation and modulate actin remodeling.
Figures







References
-
- Balch W. E., Kahn R. A., Schwaninger R. ADP-ribosylation factor is required for vesicular trafficking between the endoplasmic reticulum and the cis-Golgi compartment. J. Biol. Chem. 1992;267:13053–13061. - PubMed
-
- Balla T. Inositol-lipid binding motifs: signal integrators through protein-lipid and protein-protein interactions. J. Cell Sci. 2005;118:2093–2104. - PubMed
-
- Barrios-Rodiles M., et al. High-throughput mapping of a dynamic signaling network in mammalian cells. Science. 2005;307:1621–1625. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

