Sequential steps and checkpoints in the early exocytic compartment during secretory IgM biogenesis
- PMID: 17805346
- PMCID: PMC2230840
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7601844
Sequential steps and checkpoints in the early exocytic compartment during secretory IgM biogenesis
Abstract
The biogenesis of secretory IgM occurs stepwise under stringent quality control, formation of micro(2)L(2) preceding polymerization. How is efficiency of IgM secretion coupled to fidelity? We show here that ERp44, a soluble protein involved in thiol-mediated retention, interacts with ERGIC-53. Binding to this hexameric lectin contributes to ERp44 localization in the ER-golgi intermediate compartment. ERp44 and ERGIC-53 increase during B-lymphocyte differentiation, concomitantly with the onset of IgM polymerization. Both preferentially bind micro(2)L(2) and higher order intermediates. Their overexpression or silencing in non-lymphoid cells promotes or decreases secretion of IgM polymers, respectively. In IgM-secreting B-lymphoma cells, micro chains interact first with BiP and later with ERp44 and ERGIC-53. Our findings suggest that ERGIC-53 provides a platform that receives micro(2)L(2) subunits from the BiP-dependent checkpoint, assisting polymerization. In this process, ERp44 couples thiol-dependent assembly and quality control.
Figures

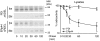
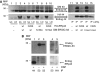
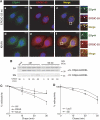
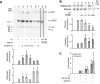



References
-
- Amitay R, Bar-Nun S, Haimovich J, Rabinovich E, Shachar I (1991) Post-translational regulation of IgM expression in B lymphocytes. Selective nonlysosomal degradation of assembled secretory IgM is temperature-dependent and occurs prior to the trans-Golgi. J Biol Chem 266: 12568–12573 - PubMed
-
- Appenzeller-Herzog C, Roche AC, Nufer O, Hauri HP (2004) pH-induced conversion of the transport lectin ERGIC-53 triggers glycoprotein release. J Biol Chem 279: 12943–12950 - PubMed
-
- Blond-Elguindi S, Cwirla SE, Dower WJ, Lipshutz RJ, Sprang SR, Sambrook JF, Gething MJ (1993) Affinity panning of a library of peptides displayed on bacteriophages reveals the binding specificity of BiP. Cell 75: 717–728 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

