Half-life of serum elimination of perfluorooctanesulfonate,perfluorohexanesulfonate, and perfluorooctanoate in retired fluorochemical production workers
- PMID: 17805419
- PMCID: PMC1964923
- DOI: 10.1289/ehp.10009
Half-life of serum elimination of perfluorooctanesulfonate,perfluorohexanesulfonate, and perfluorooctanoate in retired fluorochemical production workers
Abstract
Background: The presence of perfluorooctanesulfonate (PFOS), perfluorohexanesulfonate (PFHS), and perfluorooctanoate (PFOA) has been reported in humans and wildlife. Pharmacokinetic differences have been observed in laboratory animals.
Objective: The purpose of this observational study was to estimate the elimination half-life of PFOS, PFHS, and PFOA from human serum.
Methods: Twenty-six (24 male, 2 female) retired fluorochemical production workers, with no additional occupational exposure, had periodic blood samples collected over 5 years, with serum stored in plastic vials at -80 degrees C. At the end of the study, we used HPLC-mass spectrometry to analyze the samples, with quantification based on the ion ratios for PFOS and PFHS and the internal standard (18)O(2)-PFOS. For PFOA, quantitation was based on the internal standard (13)C(2)-PFOA.
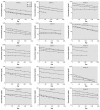
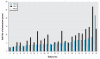
Results: THE ARITHMETIC MEAN INITIAL SERUM CONCENTRATIONS WERE AS FOLLOWS: PFOS, 799 ng/mL (range, 145-3,490); PFHS, 290 ng/mL (range, 16-1,295); and PFOA, 691 ng/mL (range, 72-5,100). For each of the 26 subjects, the elimination appeared linear on a semi-log plot of concentration versus time; therefore, we used a first-order model for estimation. The arithmetic and geometric mean half-lives of serum elimination, respectively, were 5.4 years [95% confidence interval (CI), 3.9-6.9] and 4.8 years (95% CI, 4.0-5.8) for PFOS; 8.5 years (95% CI, 6.4-10.6) and 7.3 years (95% CI, 5.8-9.2) for PFHS; and 3.8 years (95% CI, 3.1-4.4) and 3.5 years (95% CI, 3.0-4.1) for PFOA.
Conclusions: Based on these data, humans appear to have a long half-life of serum elimination of PFOS, PFHS, and PFOA. Differences in species-specific pharmacokinetics may be due, in part, to a saturable renal resorption process.
Keywords: PFHS; PFOA; PFOS; biomonitoring; perfluoroalkyl acids; perfluorohexanesulfonate; perfluorooctanesulfonate; perfluorooctanoate; pharmacokinetics.
Figures

References
-
- Andersen ME, Clewell HJ, Tan YM, Butenhoff JL, Olsen GW. Pharmacokinetic modeling of saturable, renal resorption of perfluoroalkylacids in monkeys–probing the determinants of long plasma half-lives. Toxicology. 2006;227:156–164. - PubMed
-
- Butenhoff J, Costa G, Elcombe C, Farrar D, Hansen K, Iwai H, et al. Toxicity of ammonium perfluorooctanoate (APFO) in male cynomolgus monkeys after oral dosing for six months. Toxicol Sci. 2002;69:244–257. - PubMed
-
- Butenhoff JL, Kennedy GL, Hinderliter PM, Lieder PH, Jung R, Hansen KJ, et al. Pharmacokinetics of perfluoro-octanoate (PFOA) in cynomolgus monkeys. Toxicol Sci. 2004;82:394–406. - PubMed
-
- Calafat AM, Kuklenyik Z, Reidy JA, Caudill SP, Tully JS, Needham LL. Serum concentrations of 11 polyfluoro-alkyl compounds in the U.S. population: data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) 1999–2000. Environ Sci Technol. 2007;41:2237–2242. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
