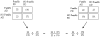Evidence of shared risk for Alzheimer's disease and Parkinson's disease using family history
- PMID: 17805588
- PMCID: PMC2679377
- DOI: 10.1007/s10048-007-0100-6
Evidence of shared risk for Alzheimer's disease and Parkinson's disease using family history
Abstract
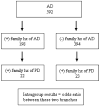
This case-control study examined the potential for a common etiology of Parkinson's disease (PD) and Alzheimer's disease (AD) using reported family history. Structured interviews were used to collect AD and PD family history from subjects (n = 1,531) with AD, PD, AD/PD, or controls. Intergroup analysis compared reported AD and PD family histories in the three case groups to the histories reported in the control group. Intragroup analysis stratified each diagnostic group based on positive family history of AD, then compared the subgroups for a family history of PD. Subjects with AD had a higher risk of having a family history of AD [odds ratio (OR) 2.3; 1.5-3.4] and subjects with PD had a higher risk of having a family history of PD (OR 2.2; 1.2-4.0) as compared to control subjects. Intergroup analyses revealed no significant crossed risk, increased risk of subjects with AD having a family history of PD vs controls and vice versa. Intragroup analysis found that subjects with PD and a family history of AD were more likely to have a family history of PD (OR 1.7; 1.1-2.6) when compared to subjects with PD and no family history of AD. A similar trend was found for subjects with AD (OR 1.7; 0.9-3.1). AD and PD cases each have an increased familial risk of their respective disease. Probands with AD or PD and a family history of either disease have a higher crossed risk of a family history of the other disease. These findings suggest the existence of common genetic and/or environmental factors that predispose to both AD and PD in the subset of cases with positive family history of both neurodegenerative diseases.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Lack of familial aggregation of Parkinson disease and Alzheimer disease.Arch Neurol. 2004 Jul;61(7):1033-9. doi: 10.1001/archneur.61.7.1033. Arch Neurol. 2004. PMID: 15262733
-
Dipeptidyl carboxypeptidase 1 (DCP1) and butyrylcholinesterase (BCHE) gene interactions with the apolipoprotein E epsilon4 allele as risk factors in Alzheimer's disease and in Parkinson's disease with coexisting Alzheimer pathology.J Med Genet. 2000 Oct;37(10):766-70. doi: 10.1136/jmg.37.10.766. J Med Genet. 2000. PMID: 11015454 Free PMC article.
-
Hospital-treated infections in early- and mid-life and risk of Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: A nationwide nested case-control study in Sweden.PLoS Med. 2022 Sep 15;19(9):e1004092. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1004092. eCollection 2022 Sep. PLoS Med. 2022. PMID: 36107840 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction between genetic and environmental risk factors for Alzheimer's disease: a reanalysis of case-control studies.Genet Epidemiol. 1994;11(6):539-51. doi: 10.1002/gepi.1370110609. Genet Epidemiol. 1994. PMID: 7713394 Review.
-
Commonalities in the genetics of Alzheimer's disease and Parkinson's disease.Expert Rev Neurother. 2008 Dec;8(12):1865-77. doi: 10.1586/14737175.8.12.1865. Expert Rev Neurother. 2008. PMID: 19086884 Review.
Cited by
-
Potential Role of Heterocyclic Aromatic Amines in Neurodegeneration.Chem Res Toxicol. 2022 Jan 17;35(1):59-72. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrestox.1c00274. Epub 2022 Jan 6. Chem Res Toxicol. 2022. PMID: 34990108 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An exploratory study on CLU, CR1 and PICALM and Parkinson disease.PLoS One. 2011;6(8):e24211. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0024211. Epub 2011 Aug 30. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21912625 Free PMC article.
-
rs3851179 Polymorphism at 5' to the PICALM Gene is Associated with Alzheimer and Parkinson Diseases in Brazilian Population.Neuromolecular Med. 2017 Sep;19(2-3):293-299. doi: 10.1007/s12017-017-8444-z. Epub 2017 May 31. Neuromolecular Med. 2017. PMID: 28567584
-
αS Oligomers Generated from Interactions with a Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid and a Dopamine Metabolite Differentially Interact with Aβ to Enhance Neurotoxicity.ACS Chem Neurosci. 2021 Nov 3;12(21):4153-4161. doi: 10.1021/acschemneuro.1c00530. Epub 2021 Oct 19. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34665617 Free PMC article.
-
Cognitive Effects of Hormone Therapy Continuation or Discontinuation in a Sample of Women at Risk for Alzheimer Disease.Am J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2015 Nov;23(11):1117-26. doi: 10.1016/j.jagp.2015.05.009. Epub 2015 May 21. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2015. PMID: 26209223 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bonifati V, Rizzu P, van Baren MJ, et al. Mutations in the DJ-1 gene associated with autosomal recessive early-onset parkinsonism. Science. 2003;299:256–259. - PubMed
-
- Gasser T, Muller-Myhsok B, Wszolek ZK, et al. A susceptibility locus for Parkinson’s disease maps to chromosome 2p13. Nat Genet. 1998;18:262–265. - PubMed
-
- Goate A, Chartier-Harlin MC, Mullan M, et al. Segregation of a missense mutation in the amyloid precursor protein gene with familial Alzheimer’s disease. Nature. 1991;349:704–706. - PubMed
-
- Kitada T, Asakawa S, Hattori N, et al. Mutations in the parkin gene cause autosomal recessive juvenile parkinsonism. Nature. 1998;392:605–608. - PubMed
-
- Levy-Lahad E, Wasco W, Poorkaj P, et al. Candidate gene for the chromosome 1 familial Alzheimer’s disease locus. Science. 1995;269:973–977. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical