Cartilage link protein 1 (Crtl1), an extracellular matrix component playing an important role in heart development
- PMID: 17822691
- PMCID: PMC2254939
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2007.07.041
Cartilage link protein 1 (Crtl1), an extracellular matrix component playing an important role in heart development
Abstract
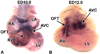
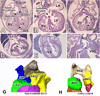
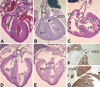
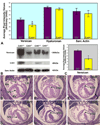
To expand our insight into cardiac development, a comparative DNA microarray analysis was performed using tissues from the atrioventricular junction (AVJ) and ventricular chambers of mouse hearts at embryonic day (ED) 10.5-11.0. This comparison revealed differential expression of approximately 200 genes, including cartilage link protein 1 (Crtl1). Crtl1 stabilizes the interaction between hyaluronan (HA) and versican, two extracellular matrix components essential for cardiac development. Immunohistochemical studies showed that, initially, Crtl1, versican, and HA are co-expressed in the endocardial lining of the heart, and in the endocardially derived mesenchyme of the AVJ and outflow tract (OFT). At later stages, this co-expression becomes restricted to discrete populations of endocardially derived mesenchyme. Histological analysis of the Crtl1-deficient mouse revealed a spectrum of cardiac malformations, including AV septal and myocardial defects, while expression studies showed a significant reduction in versican levels. Subsequent analysis of the hdf mouse, which carries an insertional mutation in the versican gene (CSPG2), demonstrated that haploinsufficient versican mice display septal defects resembling those seen in Crtl1(-/-) embryos, suggesting that reduced versican expression may contribute to a subset of the cardiac abnormalities observed in the Crtl1(-/-) mouse. Combined, these findings establish an important role for Crtl1 in heart development.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




Similar articles
-
Mef2c regulates transcription of the extracellular matrix protein cartilage link protein 1 in the developing murine heart.PLoS One. 2013;8(2):e57073. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0057073. Epub 2013 Feb 26. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23468913 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular cloning and developmental expression of a hyaluronan and proteoglycan link protein gene, crtl1/hapln1, in zebrafish.Zoolog Sci. 2008 Sep;25(9):912-8. doi: 10.2108/zsj.25.912. Zoolog Sci. 2008. PMID: 19267601
-
Localization of cartilage linking protein 1 during primary neurulation in the chick embryo.Brain Res Dev Brain Res. 2003 Mar 14;141(1-2):141-8. doi: 10.1016/s0165-3806(03)00011-7. Brain Res Dev Brain Res. 2003. PMID: 12644258
-
Hyaluronic acid and hyaluronic acid-binding proteins in brain extracellular matrix.Anat Embryol (Berl). 1993 Nov;188(5):419-33. doi: 10.1007/BF00190136. Anat Embryol (Berl). 1993. PMID: 7508695 Review.
-
[Cartilage proteoglycan aggregate: structure and function].Clin Calcium. 2004 Jul;14(7):9-14. Clin Calcium. 2004. PMID: 15577070 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Genetic reduction of the extracellular matrix protein versican attenuates inflammatory cell infiltration and improves contractile function in dystrophic mdx diaphragm muscles.Sci Rep. 2020 Jul 6;10(1):11080. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-67464-x. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32632164 Free PMC article.
-
Mef2c regulates transcription of the extracellular matrix protein cartilage link protein 1 in the developing murine heart.PLoS One. 2013;8(2):e57073. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0057073. Epub 2013 Feb 26. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23468913 Free PMC article.
-
Flow-Induced Transcriptomic Remodeling of Endothelial Cells Derived From Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells.Front Physiol. 2020 Oct 15;11:591450. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2020.591450. eCollection 2020. Front Physiol. 2020. PMID: 33178051 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of a limb-specific regulatory element in the promoter of the link protein gene.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2019 Oct 22;518(4):672-677. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2019.08.104. Epub 2019 Aug 27. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2019. PMID: 31470976 Free PMC article.
-
HAPLN1 Affects Cell Viability and Promotes the Pro-Inflammatory Phenotype of Fibroblast-Like Synoviocytes.Front Immunol. 2022 Jun 2;13:888612. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.888612. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35720292 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Binette F, Cravens J, Kahoussi B, Haudenschild DR, Goetinck PF. Link protein is ubiquitously expressed in non-cartilaginous tissues where it enhances and stabilizes the interaction of proteoglycans with hyaluronic acid. J Biol Chem. 1994;269:19116–19122. - PubMed
-
- Bushdid PB, Osinska H, Waclaw RR, Molkentin JD, Yutzey KE. NFATc3 and NFATc4 are required for cardiac development and mitochondrial function. Circ Res. 2003;92:1305–1313. - PubMed
-
- Camenisch TD, Spicer AP, Brehm-Gibson T, Biesterfeldt J, Augustine ML, Calabro A, Jr, Kubalak S, Klewer SE, McDonald JA. Disruption of hyaluronan synthase-2 abrogates normal cardiac morphogenesis and hyaluronan-mediated transformation of epithelium to mesenchyme. J Clin Invest. 2000;106:349–360. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Campione M, Ros MA, Icardo JM, Piedra E, Christoffels VM, Schweickert A, Blum M, Franco D, Moorman AF. Pitx2 expression defines a left cardiac lineage of cells: evidence for atrial and ventricular molecular isomerism in the iv/iv mice. Dev Biol. 2001;231:252–264. - PubMed
-
- Caterson B, Baker JR, Christner JE, Lee Y, Lentz M. Monoclonal antibodies as probes for determining the microheterogeneity of the link proteins of cartilage proteoglycan. J Biol Chem. 1985;260:11348–11356. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

