The ligand occupancy of endothelial protein C receptor switches the protease-activated receptor 1-dependent signaling specificity of thrombin from a permeability-enhancing to a barrier-protective response in endothelial cells
- PMID: 17823308
- PMCID: PMC2190610
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2007-06-096651
The ligand occupancy of endothelial protein C receptor switches the protease-activated receptor 1-dependent signaling specificity of thrombin from a permeability-enhancing to a barrier-protective response in endothelial cells
Abstract
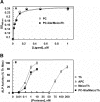
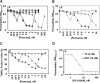
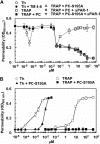
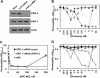
Recent studies have indicated that activated protein C (APC) may exert its cytoprotective and anti-inflammatory activities through the endothelial protein C receptor (EPCR)-dependent cleavage of protease-activated receptor 1 (PAR-1) on vascular endothelial cells. Noting that (1) the activation of protein C on endothelial cells requires thrombin, (2) relative to APC, thrombin cleaves PAR-1 with approximately 3 to 4 orders of magnitude higher catalytic efficiency, and (3) PAR-1 is a target for the proinflammatory activity of thrombin, it is not understood how APC can elicit a protective signaling response through the cleavage of PAR-1 when thrombin is present. In this study, we demonstrate that EPCR is associated with caveolin-1 in lipid rafts of endothelial cells and that its occupancy by the gamma-carboxyglutamic acid (Gla) domain of protein C/APC leads to its dissociation from caveolin-1 and recruitment of PAR-1 to a protective signaling pathway through coupling of PAR-1 to the pertussis toxin-sensitive G(i)-protein. Thus, when EPCR is bound by protein C, the PAR-1 cleavage-dependent protective signaling responses in endothelial cells can be mediated by either thrombin or APC. These results provide a new paradigm for understanding how PAR-1 and EPCR participate in protective signaling events in endothelial cells.
Figures

References
-
- Esmon CT. Molecular events that control the protein C anticoagulant pathway. Thromb Haemost. 1993;70:29–35. - PubMed
-
- Stenflo J. Structure and function of protein C. Semin Thromb Hemost. 1984;10:109–121. - PubMed
-
- Walker FJ, Fay PJ. Regulation of blood coagulation by the protein C system. FASEB J. 1992;6:2561–2567. - PubMed
-
- Dahlbäck B. Protein S and C4b-binding protein: Components involved in the regulation of the protein C anticoagulant system. Thromb Haemost. 1991;66:49–61. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

