Crystal structure of a thermally stable rhodopsin mutant
- PMID: 17825322
- PMCID: PMC2258155
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jmb.2007.03.007
Crystal structure of a thermally stable rhodopsin mutant
Abstract
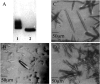
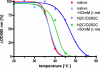
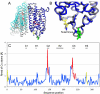
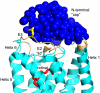
We determined the structure of the rhodopsin mutant N2C/D282C expressed in mammalian cells; the first structure of a recombinantly produced G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR). The mutant was designed to form a disulfide bond between the N terminus and loop E3, which allows handling of opsin in detergent solution and increases thermal stability of rhodopsin by 10 deg.C. It allowed us to crystallize a fully deglycosylated rhodopsin (N2C/N15D/D282C). N15 mutations are normally misfolding and cause retinitis pigmentosa in humans. Microcrystallographic techniques and a 5 microm X-ray beam were used to collect data along a single needle measuring 5 microm x 5 microm x 90 microm. The disulfide introduces only minor changes but fixes the N-terminal cap over the beta-sheet lid covering the ligand-binding site, a likely explanation for the increased stability. This work allows structural investigation of rhodopsin mutants and shows the problems encountered during structure determination of GPCRs and other mammalian membrane proteins.
Figures

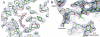
References
-
- Drews J, Ryser S. The role of innovation in drug development. Nat Biotechnol. 1997;15:1318–9. - PubMed
-
- Palczewski K, Kumasaka T, Hori T, Behnke CA, Motoshima H, Fox BA, Le Trong I, Teller DC, Okada T, Stenkamp RE, Yamamoto M, Miyano M. Crystal structure of rhodopsin: A G protein-coupled receptor. Science. 2000;289:739–45. - PubMed
-
- Okada T, Sugihara M, Bondar AN, Elstner M, Entel P, Buss V. The retinal conformation and its environment in rhodopsin in light of a new 2.2 A crystal structure. J Mol Biol. 2004;342:571–83. - PubMed
-
- Li J, Edwards PC, Burghammer M, Villa C, Schertler GF. Structure of bovine rhodopsin in a trigonal crystal form. J Mol Biol. 2004;343:1409–38. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

