Wave aberrations in rhesus monkeys with vision-induced ametropias
- PMID: 17825347
- PMCID: PMC2094213
- DOI: 10.1016/j.visres.2007.07.014
Wave aberrations in rhesus monkeys with vision-induced ametropias
Abstract
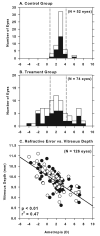
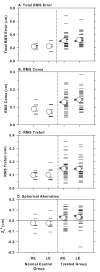
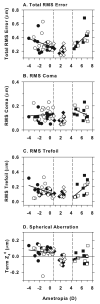
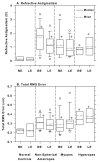
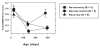
The purpose of this study was to investigate the relationship between refractive errors and high-order aberrations in infant rhesus monkeys. Specifically, we compared the monochromatic wave aberrations measured with a Shack-Hartman wavefront sensor between normal monkeys and monkeys with vision-induced refractive errors. Shortly after birth, both normal monkeys and treated monkeys reared with optically induced defocus or form deprivation showed a decrease in the magnitude of high-order aberrations with age. However, the decrease in aberrations was typically smaller in the treated animals. Thus, at the end of the lens-rearing period, higher than normal amounts of aberrations were observed in treated eyes, both hyperopic and myopic eyes and treated eyes that developed astigmatism, but not spherical ametropias. The total RMS wavefront error increased with the degree of spherical refractive error, but was not correlated with the degree of astigmatism. Both myopic and hyperopic treated eyes showed elevated amounts of coma and trefoil and the degree of trefoil increased with the degree of spherical ametropia. Myopic eyes also exhibited a much higher prevalence of positive spherical aberration than normal or treated hyperopic eyes. Following the onset of unrestricted vision, the amount of high-order aberrations decreased in the treated monkeys that also recovered from the experimentally induced refractive errors. Our results demonstrate that high-order aberrations are influenced by visual experience in young primates and that the increase in high-order aberrations in our treated monkeys appears to be an optical byproduct of the vision-induced alterations in ocular growth that underlie changes in refractive error. The results from our study suggest that the higher amounts of wave aberrations observed in ametropic humans are likely to be a consequence, rather than a cause, of abnormal refractive development.
Figures


References
-
- Artal P, Benito A, Tabernero J. The human eye is an example of robust optical design. Journal of Vision. 2006;6:1–7. http://journalofvision.org/6/1/1/ - PubMed
-
- Artal P, Guirao A, Berrio E, Williams DR. Compensation of corneal aberrations by the internal optics in the human eye. Journal of Vision. 2001;1:1–8. - PubMed
-
- Atchison DA. Anterior corneal and internal contributions to peripheral aberrations of human eyes. Journal of Optical Society of America A, Optics, Images, Science, and Vision. 2004;21:355–359. - PubMed
-
- Atchison DA, Pritchard N, Schmid KL, Scott DH, Jones CE, Pope JM. Shape of the retinal surface in emmetropia and myopia. Investigative Ophthalmology and Vision Science. 2005;46:2698–2707. - PubMed
-
- Bansal J, Coletta NJ, Moskowitz A, Han H. Pupil displacement in corneal topography images is related to the eye's refractive error. Investigative Ophthalmology and Vision Science. 2004;45(Suppl) ARVO E-Abstract nr 2762.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

