The effects of Arcanobacterium pyogenes on endometrial function in vitro, and on uterine and ovarian function in vivo
- PMID: 17825901
- PMCID: PMC2702129
- DOI: 10.1016/j.theriogenology.2007.07.013
The effects of Arcanobacterium pyogenes on endometrial function in vitro, and on uterine and ovarian function in vivo
Abstract
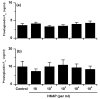
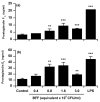
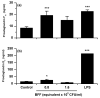
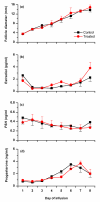
Uterine bacterial infection after parturition causes endometritis, perturbs ovarian function and leads to infertility in cattle. Although endometritis is caused by mixed infections, endometrial pathology is associated with the presence of Arcanobacterium pyogenes. The aims of the present study were to determine the effects of A. pyogenes on endometrial function in vitro, and on uterine and ovarian function in vivo. Heat-killed A. pyogenes did not affect the production of prostaglandin F2alpha (PGF) or prostaglandin E(2) (PGE) from endometrial explants, or purified populations of endometrial epithelial or stromal cells. However, the explants produced more PGF and PGE than controls when treated with a bacteria-free filtrate (BFF) cultured from A. pyogenes. Similarly, BFF stimulated PGF and PGE production by epithelial and stromal cells, respectively. So, BFF or control PBS was infused into the uterus of heifers (n=7 per group) for 8 days, starting the day after estrus. Emergence of the follicle wave, dominant follicle or corpus luteum diameter, and peripheral plasma FSH, LH, estradiol, progesterone, PGFM, or acute phase protein concentrations were unaffected by the BFF infusion. In the live animal it is likely that the intact uterine mucosa limits the exposure of the endometrial cells to the exotoxin of A. pyogenes, whereas the cells are readily exposed to the toxin in vitro.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Differential endometrial cell sensitivity to a cholesterol-dependent cytolysin links Trueperella pyogenes to uterine disease in cattle.Biol Reprod. 2014 Mar 13;90(3):54. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod.113.115972. Print 2014 Mar. Biol Reprod. 2014. PMID: 24478394
-
Influence of experimental intrauterine infusion of Arcanobacterium pyogenes solution on ovarian activity in cycling cows.J Vet Med Sci. 2008 Jan;70(1):77-83. doi: 10.1292/jvms.70.77. J Vet Med Sci. 2008. PMID: 18250576
-
A model of clinical endometritis in Holstein heifers using pathogenic Escherichia coli and Trueperella pyogenes.J Dairy Sci. 2019 Mar;102(3):2686-2697. doi: 10.3168/jds.2018-15595. Epub 2019 Jan 26. J Dairy Sci. 2019. PMID: 30692014 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of infertility associated with clinical and subclinical endometritis in high producing dairy cattle.Reprod Domest Anim. 2009 Sep;44 Suppl 3:1-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1439-0531.2009.01465.x. Reprod Domest Anim. 2009. PMID: 19660075 Review.
-
Uterine diseases in cattle after parturition.Vet J. 2008 Apr;176(1):115-21. doi: 10.1016/j.tvjl.2007.12.031. Epub 2008 Mar 7. Vet J. 2008. PMID: 18329302 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
An Advanced Understanding of Uterine Microbial Ecology Associated with Metritis in Dairy Cows.Genomics Inform. 2018 Dec;16(4):e21. doi: 10.5808/GI.2018.16.4.e21. Epub 2018 Dec 28. Genomics Inform. 2018. PMID: 30602082 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of native Escherichia coli populations from bovine vagina of healthy heifers and cows with postpartum uterine disease.PLoS One. 2020 Jun 1;15(6):e0228294. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0228294. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32479536 Free PMC article.
-
Bovine Endometrial Epithelial Cells Scale Their Pro-inflammatory Response In vitro to Pathogenic Trueperella pyogenes Isolated from the Bovine Uterus in a Strain-Specific Manner.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2017 Jun 21;7:264. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2017.00264. eCollection 2017. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28680854 Free PMC article.
-
Diversity and succession of bacterial communities in the uterine fluid of postpartum metritic, endometritic and healthy dairy cows.PLoS One. 2012;7(12):e53048. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0053048. Epub 2012 Dec 27. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23300859 Free PMC article.
-
Associations between the clinical signs of chronic endometritis with ovarian cysts and body condition loss in German Holstein Friesian cows.J Vet Sci. 2009 Dec;10(4):337-41. doi: 10.4142/jvs.2009.10.4.337. J Vet Sci. 2009. PMID: 19934600 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sheldon IM, Lewis GS, LeBlanc SJ, Gilbert RO. Defining postpartum uterine disease in cattle. Theriogenology. 2006;65:1516–1530. - PubMed
-
- Sheldon IM, Noakes DE, Rycroft AN, Pfeiffer DU, Dobson H. Influence of uterine bacterial contamination after parturition on ovarian dominant follicle selection and follicle growth and function in cattle. Reproduction. 2002;123:837–845. - PubMed
-
- Borsberry S, Dobson H. Periparturient diseases and their effect on reproductive performance in five dairy herds. Veterinary Record. 1989;124:217–219. - PubMed
-
- LeBlanc SJ, Duffield TF, Leslie KE, Bateman KG, Keefe GP, Walton JS, Johnson WH. Defining and diagnosing postpartum clinical endometritis and its impact on reproductive performance in dairy cows. Journal of Dairy Science. 2002;85:2223–2236. - PubMed
-
- McDougall S. Effect of intrauterine antibiotic treatment on reproductive performance of dairy cows following periparturient disease. New Zealand Veterinary Journal. 2001;49:150–158. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

