The growth hormone-insulin-like growth factor-I axis in chronic kidney disease
- PMID: 17826224
- PMCID: PMC2706146
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ghir.2007.07.009
The growth hormone-insulin-like growth factor-I axis in chronic kidney disease
Abstract
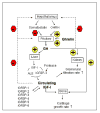
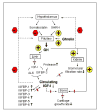
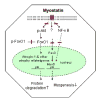
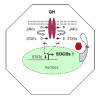
Growth hormone (GH) and insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) are important physiologic regulators of growth, body composition, and kidney function. Perturbations in the GH-IGF-I axis are responsible for many important complications seen in chronic kidney disease (CKD), such as growth retardation and cachectic wasting, as well as disease progression. Recent evidence suggests that CKD is characterized by abnormalities in GH and IGF-I signal transduction and the interaction of these pathways with those that involve other molecules such as ghrelin, myostatin, and the suppressor of cytokine signaling (SOCS) family. Further understanding of GH/IGF pathophysiology in CKD may lead to the development of therapeutic strategies for these devastating complications, which are associated with high rates of mortality and morbidity.
Figures
References
-
- Mak RH. Chronic kidney disease in children: state of the art. Pediatr Nephrol. 2006 EPUB Nov 4. - PubMed
-
- Kaskel F. Chronic renal disease: A growing problem. Kidney Int. 2003;64:1141–1151. - PubMed
-
- Tonshoff B, Blum WF, Mehls O. Derangements of the somatotropic hormone axis in chronic renal failure. Kidney Int. 1997;S58:S106–S113. - PubMed
-
- Wuhl E, Schaefer F. Effects of growth hormone in patients with chronic renal failure: experience in children and adults. Horm Res. 2002;3:35–38. - PubMed
-
- Mak RH, Pak Y. End-organ resistance to growth hormone and IGF-I in epiphyseal chondrocytes of uremic rats. Kidney Int. 1996;50:400–406. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

