Ethnic heterogeneity in the longitudinal effects of placental vascular blood flow on birthweight
- PMID: 17826729
- PMCID: PMC2278234
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajog.2007.05.043
Ethnic heterogeneity in the longitudinal effects of placental vascular blood flow on birthweight
Abstract
Objective: Our goals were: (1) to estimate the longitudinal trends in uterine artery (UtArt) and umbilical artery (UmArt) resistance indices (RIs) in different ethnic strata; (2) to estimate time-dependent changes across gestation in the influence of variation in UtArt and UmArt RI on variation in birthweight in different ethnic strata; and (3) to determine the optimum set of UtArt and UmArt RIs for predicting birthweight in different ethnic strata.
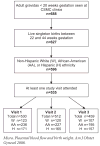
Study design: Analyses were carried out on data collected in a prospective study of 535 multiethnic gravidas recruited from the Cedars-Sinai Medical Center (Los Angeles, CA). Baseline maternal characteristics were recorded at time of entry into the study. UtArt and UmArt RIs were measured on 3 occasions during pregnancy (visit 1, 16-20 weeks' gestation; visit 2, 21-29 weeks' gestation; and visit 3, 30-36 weeks' gestation). The outcome for this study was gestational age-adjusted birthweight (aBW).
Results: The average UtArt and UmArt RI decreased steadily across gestation for all ethnicities. The average UtArt RI at each visit and the average rate of change between visits were not significantly different among the ethnicities. However, the UmArt RI measured at visit 3 and its rate of change in the last trimester were significantly different among the ethnic groups (P < .02). After adjustment for traditional risk factors for fetal growth restriction, the magnitude and rate of change of UtArt RI significantly predicted aBW only in Hispanic women, whereas the magnitude and rate of change of UmArt RI predicted aBW only in African American women. The most parsimonious combination of UtArt and UmArt RI measurements at visits 1, 2, and 3 that predicted statistically significant variation in aBW differed by ethnicity.
Conclusion: The relationships between aBW and longitudinally collected measures of UtArt and UmArt RI depend on the context defined by ethnicity and time of measurement after adjusting for a parsimoniously selected subset of traditional risk factors.
Similar articles
-
Placental blood flow and the risk of preterm delivery.Placenta. 2009 Jul;30(7):619-24. doi: 10.1016/j.placenta.2009.04.007. Epub 2009 May 21. Placenta. 2009. PMID: 19464055 Free PMC article.
-
Changes in Doppler flow velocity waveforms and fetal size at 20 weeks gestation among cigarette smokers.BJOG. 2009 Sep;116(10):1300-6. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-0528.2009.02266.x. Epub 2009 Jun 29. BJOG. 2009. PMID: 19566582
-
[A multi-center study to evaluate the dynamic changes of uterine artery and umbilical artery flow in a normal pregnancy and hypertensive disorders in pregnancy].Zhonghua Fu Chan Ke Za Zhi. 2010 Aug;45(8):583-7. Zhonghua Fu Chan Ke Za Zhi. 2010. PMID: 21029613 Chinese.
-
Folic acid supplementation and malaria susceptibility and severity among people taking antifolate antimalarial drugs in endemic areas.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Feb 1;2(2022):CD014217. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD014217. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36321557 Free PMC article.
-
Spiral artery blood flow during pregnancy: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2020 Nov 11;20(1):680. doi: 10.1186/s12884-020-03150-0. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2020. PMID: 33176723 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Placental blood flow and the risk of preterm delivery.Placenta. 2009 Jul;30(7):619-24. doi: 10.1016/j.placenta.2009.04.007. Epub 2009 May 21. Placenta. 2009. PMID: 19464055 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alexander GR, Kogan MD, Himes JH. 1994-1996 U.S. singleton birthweight percentiles for gestational age by race, Hispanic origin, and gender. Matern Child Health J. 1999;3:225–31. - PubMed
-
- Alexander GR, Kogan MD, Himes JH, Mor JM, Goldenberg R. Racial differences in birthweight for gestational age and infant mortality in extremely-low-risk US populations. Paediatr Perinat Epidemiol. 1999;13:205–17. - PubMed
-
- Regnault TR, Galan HL, Parker TA, Anthony RV. Placental development in normal and compromised pregnancies—a review. Placenta. 2002;23(Suppl A):S119–29. - PubMed
-
- Kingdom J, Huppertz B, Seaward G, Kaufmann P. Development of the placental villous tree and its consequences for fetal growth. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2000;92:35–43. - PubMed
-
- Brosens I, Dixon HG, Robertson WB. Fetal growth retardation and the arteries of the placental bed. Br J Obstet Gynaecol. 1977;84:656–63. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical