The p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway in rheumatoid arthritis
- PMID: 17827184
- PMCID: PMC2754165
- DOI: 10.1136/ard.2007.074278
The p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway in rheumatoid arthritis
Abstract
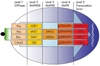
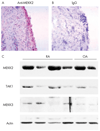
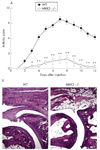
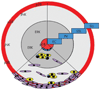
Chronic inflammatory processes are based on a sustained and tightly regulated communication network among different cells types. This network comprises extracellular mediators such as cytokines, chemokines and matrix-degrading proteases, which orchestrate the participation of cells in the chronic inflammatory process. The mirrors of this outside communication world are intracellular transcription factor pathways, which shuttle information about inflammatory stimuli to the cell nucleus. This review examines the function of one key signal transduction pathway of inflammation--the p38 mitogen-activated protein kinases (p38MAPK). The signalling pathway is considered as crucial for the induction and maintenance of chronic inflammation, and its components thus emerge as interesting molecular targets of small molecule inhibitors for controlling inflammation. This review not only summarises the current knowledge of activation, regulation and function of the p38MAPK pathway but also examines the role of this pathway in clinical disease. It gives an overview of current evidence of p38MAPK activation in inflammatory arthritis and elaborates the key molecular determinants which contribute to p38MAPK activation in joint disease.
Figures
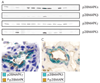

References
-
- Cohen DM. Mitogen-activated protein kinase cascades and the signaling of hyperosmotic stress to immediate early genes. Comp Biochem Physiol. 1997;117:291–299. - PubMed
-
- Johnson GL, Lapadat R. Mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways mediated by ERK, JNK, and p38 protein kinases. Science. 2002;298:1911–1912. - PubMed
-
- Sweeney SE, Firestein GS. Signal transduction in rheumatoid arthritis. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2004;16:231–237. - PubMed
-
- Schett G, Tohidast-Akrad M, Smolen JS, Schmid BJ, Steiner CW, Bitzan P, et al. Activation, differential localization, and regulation of the stress-activated protein kinases, extracellular signal-regulated kinase, c-JUN N-terminal kinase, and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase, in synovial tissue and cells in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2000;43:2501–2512. - PubMed
-
- Lee JC, Laydon JT, McDonnell PC, Gallagher TF, Kumar S, Green D, et al. A protein kinase involved in the regulation of inflammatory cytokine biosynthesis. Nature. 1994;372:739–746. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

