Vitamin H-regulated transgene expression in mammalian cells
- PMID: 17827215
- PMCID: PMC2034481
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkm466
Vitamin H-regulated transgene expression in mammalian cells
Abstract
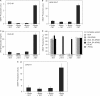
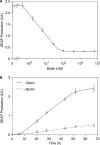
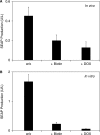
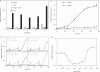
Although adjustable transgene expression systems are considered essential for future therapeutic and biopharmaceutical manufacturing applications, the currently available transcription control modalities all require side-effect-prone inducers such as immunosupressants, hormones and antibiotics for fine-tuning. We have designed a novel mammalian transcription-control system, which is reversibly fine-tuned by non-toxic vitamin H (also referred to as biotin). Ligation of vitamin H, by engineered Escherichia coli biotin ligase (BirA), to a synthetic biotinylation signal fused to the tetracycline-dependent transactivator (tTA), enables heterodimerization of tTA to a streptavidin-linked transrepressor domain (KRAB), thereby abolishing tTA-mediated transactivation of specific target promoters. As heterodimerization of tTA to KRAB is ultimately conditional upon the presence of vitamin H, the system is vitamin H responsive. Transgenic Chinese hamster ovary cells, engineered for vitamin H-responsive gene expression, showed high-level, adjustable and reversible production of a human model glycoprotein in bench-scale culture systems, bioreactor-based biopharmaceutical manufacturing scenarios, and after implantation into mice. The vitamin H-responsive expression systems showed unique band pass filter-like regulation features characterized by high-level expression at low (0-2 nM biotin), maximum repression at intermediate (100-1000 nM biotin), and high-level expression at increased (>100 000 nM biotin) biotin concentrations. Sequential ON-to-OFF-to-ON, ON-to-OFF and OFF-to-ON expression profiles with graded expression transitions can all be achieved by simply increasing the level of a single inducer molecule without exchanging the culture medium. These novel expression characteristics mediated by an FDA-licensed inducer may foster advances in therapeutic cell engineering and manufacturing of difficult-to-produce protein therapeutics.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A novel vector platform for vitamin H-inducible transgene expression in mammalian cells.J Biotechnol. 2007 Aug 31;131(2):150-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiotec.2007.06.008. Epub 2007 Jun 23. J Biotechnol. 2007. PMID: 17669538
-
A synthetic time-delay circuit in mammalian cells and mice.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007 Feb 20;104(8):2643-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0606398104. Epub 2007 Feb 12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007. PMID: 17296937 Free PMC article.
-
Artificial regulatory networks and cascades for discrete multilevel transgene control in mammalian cells.Biotechnol Bioeng. 2003 Sep 30;83(7):810-20. doi: 10.1002/bit.10731. Biotechnol Bioeng. 2003. PMID: 12889021
-
Tetracycline-regulated mouse models of cancer.Cold Spring Harb Protoc. 2014 Oct 1;2014(10):pdb.top069823. doi: 10.1101/pdb.top069823. Cold Spring Harb Protoc. 2014. PMID: 25275112 Review.
-
Biotin sensing: universal influence of biotin status on transcription.Annu Rev Genet. 2007;41:443-64. doi: 10.1146/annurev.genet.41.042007.170450. Annu Rev Genet. 2007. PMID: 17669049 Review.
Cited by
-
Small-molecule inducible transcriptional control in mammalian cells.Crit Rev Biotechnol. 2020 Dec;40(8):1131-1150. doi: 10.1080/07388551.2020.1808583. Epub 2020 Aug 30. Crit Rev Biotechnol. 2020. PMID: 32862714 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cosmetics-triggered percutaneous remote control of transgene expression in mice.Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Aug 18;43(14):e91. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv326. Epub 2015 May 5. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015. PMID: 25943548 Free PMC article.
-
A versatile bioelectronic interface programmed for hormone sensing.Nat Commun. 2023 May 31;14(1):3151. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-39015-1. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 37258547 Free PMC article.
-
An electrogenetic interface to program mammalian gene expression by direct current.Nat Metab. 2023 Aug;5(8):1395-1407. doi: 10.1038/s42255-023-00850-7. Epub 2023 Jul 31. Nat Metab. 2023. PMID: 37524785 Free PMC article.
-
Controlling transgene expression in subcutaneous implants using a skin lotion containing the apple metabolite phloretin.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009 Jun 30;106(26):10638-43. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0901501106. Epub 2009 Jun 22. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009. PMID: 19549857 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kramer BP, Fischer C, Fussenegger M. BioLogic gates enable logical transcription control in mammalian cells. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2004;87:478–484. - PubMed
-
- Kramer BP, Viretta AU, Daoud-El-Baba M, Aubel D, Weber W, Fussenegger M. An engineered epigenetic transgene switch in mammalian cells. Nat. Biotechnol. 2004;22:867–870. - PubMed
-
- Kramer BP, Weber W, Fussenegger M. Artificial regulatory networks and cascades for discrete multilevel transgene control in mammalian cells. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2003;83:810–820. - PubMed
-
- McLoughlin JM, McCarty TM, Cunningham C, Clark V, Senzer N, Nemunaitis J, Kuhn JA. TNFerade, an adenovector carrying the transgene for human tumor necrosis factor alpha, for patients with advanced solid tumors: surgical experience and long-term follow-up. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2005;12:825–830. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

