Toward full-sequence de novo protein design with flexible templates for human beta-defensin-2
- PMID: 17827237
- PMCID: PMC2157230
- DOI: 10.1529/biophysj.107.110627
Toward full-sequence de novo protein design with flexible templates for human beta-defensin-2
Abstract
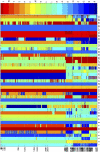
In this article, we introduce and apply our de novo protein design framework, which observes true backbone flexibility, to the redesign of human beta-defensin-2, a 41-residue cationic antimicrobial peptide of the innate immune system. The flexible design templates are generated using molecular dynamics simulations with both Generalized Born implicit solvation and explicit water molecules. These backbone templates were employed in addition to the x-ray crystal structure for designing human beta-defensin-2. The computational efficiency of our framework was demonstrated with the full-sequence design of the peptide with flexible backbone templates, corresponding to the mutation of all positions except the native cysteines.
Figures



References
-
- Fernandez-Lopez, S., H. Kim, E. C. Choi, M. Delgado, J. R. Granja, A. Khasanov, K. Kraehenbuehl, G. Long, D. A. Weinberger, K. M. Wilcoxen, and M. R. Ghadiri. 2001. Antibacterial agents based on the cyclic D,L-α-peptide architecture. Nature. 412:452–455. - PubMed
-
- Nizet, V., T. Ohtake, X. Lauth, J. Trowbridge, J. Rudisill, R. A. Dorschner, V. Pestonjamasp, J. Piranino, K. Huttner, and R. L. Gallo. 2001. Innate antimicrobial peptide protects the skin from invasive bacterial infection. Nature. 414:454–457. - PubMed
-
- Zasloff, M. 2002. Antimicrobial peptides of multicellular organisms. Nature. 415:389–395. - PubMed
-
- Ganz, T. 2003. Defensins: antimicrobial peptides of innate immunity. Nature. 3:710–720. - PubMed
-
- Mygind, P. H., R. L. Fischer, K. M. Schnorr, M. T. Hansen, C. P. Sönksen, S. Ludvigsen, D. Raventós, S. Buskov, B. Christensen, L. D. Maria, O. Taboureau, D. Yaver, S. G. Elvig-Jørgensen, M. V. Sørensen, B. E. Christensen, S. Kjærulff, N. Frimodt-Moller, R. I. Lehrer, M. Zasloff, and H.-H. Kristensen. 2005. Plectasin is a peptide antibiotic with therapeutic potential from a saprophytic fungus. Nature. 437:975–980. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

