High-resolution timing of cell cycle-regulated gene expression
- PMID: 17827275
- PMCID: PMC2040468
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0706022104
High-resolution timing of cell cycle-regulated gene expression
Abstract
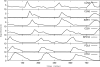
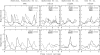
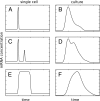
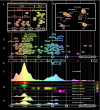
The eukaryotic cell division cycle depends on an intricate sequence of transcriptional events. Using an algorithm based on maximum-entropy deconvolution, and expression data from a highly synchronized yeast culture, we have timed the peaks of expression of transcriptionally regulated cell cycle genes to an accuracy of 2 min (approximately equal to 1% of the cell cycle time). The set of 1,129 cell cycle-regulated genes was identified by a comprehensive analysis encompassing all available cell cycle yeast data sets. Our results reveal distinct subphases of the cell cycle undetectable by morphological observation, as well as the precise timeline of macromolecular complex assembly during key cell cycle events.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: S.L.M. declares a conflict of interest (such as defined by PNAS policy). “The manuscript titled ‘High-resolution timing of cell cycle-regulated gene expression’ is coauthored by a group of scientists working in the Department of Biochemistry that I chair here at University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center. I am highly familiar with the research because it makes extensive use of data coming from my own laboratory.”
Figures
Similar articles
-
A general approach to the isolation of cell cycle-regulated genes in the budding yeast, Saccharomyces cerevisiae.J Mol Biol. 1991 Apr 5;218(3):543-56. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90700-g. J Mol Biol. 1991. PMID: 2016745
-
New weakly expressed cell cycle-regulated genes in yeast.Yeast. 2005 Nov;22(15):1191-201. doi: 10.1002/yea.1302. Yeast. 2005. PMID: 16278933
-
Transcriptional regulatory networks in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Science. 2002 Oct 25;298(5594):799-804. doi: 10.1126/science.1075090. Science. 2002. PMID: 12399584
-
A regulatory hierarchy for cell specialization in yeast.Nature. 1989 Dec 14;342(6251):749-57. doi: 10.1038/342749a0. Nature. 1989. PMID: 2513489 Review.
-
Cell cycle regulated gene expression in yeasts.Adv Genet. 2011;73:51-85. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-380860-8.00002-1. Adv Genet. 2011. PMID: 21310294 Review.
Cited by
-
Developmental series of gene expression clarifies maternal mRNA provisioning and maternal-to-zygotic transition in a reef-building coral.BMC Genomics. 2021 Nov 11;22(1):815. doi: 10.1186/s12864-021-08114-y. BMC Genomics. 2021. PMID: 34763678 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptional responses to DNA damage.DNA Repair (Amst). 2019 Jul;79:40-49. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2019.05.002. Epub 2019 May 7. DNA Repair (Amst). 2019. PMID: 31102970 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Systematic identification of yeast cell cycle transcription factors using multiple data sources.BMC Bioinformatics. 2008 Dec 5;9:522. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-9-522. BMC Bioinformatics. 2008. PMID: 19061501 Free PMC article.
-
Branching process deconvolution algorithm reveals a detailed cell-cycle transcription program.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013 Mar 5;110(10):E968-77. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1120991110. Epub 2013 Feb 6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013. PMID: 23388635 Free PMC article.
-
Characterizing regulatory path motifs in integrated networks using perturbational data.Genome Biol. 2010;11(3):R32. doi: 10.1186/gb-2010-11-3-r32. Epub 2010 Mar 11. Genome Biol. 2010. PMID: 20230615 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cho RJ, Campbell MDI, Winzeler EA, Steinmetz L, Conway A, Wodicka L, Wolfsberg TG, Gabrielian AE, Landsman D, Lockhart DJ, Davis RW. Mol Cell. 1998;2:65–73. - PubMed
-
- Cho RJ, Huang MX, Campbell MJ, Dong HL, Steinmetz L, Sapinoso L, Hampton G, Elledge SJ, Davis RW, Lockhart DJ. Nat Genet. 2001;27:48–54. - PubMed
-
- Rustici G, Mata J, Kivinen K, Lio P, Penkett CJ, Burns G, Hayles J, Brazma A, Nurse P, Bahler J. Nat Genet. 2004;36:809–817. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

