The pinholin of lambdoid phage 21: control of lysis by membrane depolarization
- PMID: 17827300
- PMCID: PMC2168629
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.00847-07
The pinholin of lambdoid phage 21: control of lysis by membrane depolarization
Abstract
The phage 21 holin, S(21), forms small membrane holes that depolarize the membrane and is designated as a pinholin, as opposed to large-hole-forming holins, like S(lambda). Pinholins require secreted SAR endolysins, a pairing that may represent an intermediate in the evolution of canonical holin-endolysin systems.
Figures
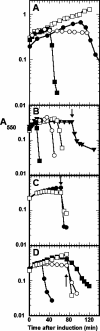

Similar articles
-
Visualization of pinholin lesions in vivo.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013 May 28;110(22):E2054-63. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1222283110. Epub 2013 May 13. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013. PMID: 23671069 Free PMC article.
-
Stable micron-scale holes are a general feature of canonical holins.Mol Microbiol. 2014 Jan;91(1):57-65. doi: 10.1111/mmi.12439. Epub 2013 Nov 21. Mol Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 24164554 Free PMC article.
-
Phage Lysis: Multiple Genes for Multiple Barriers.Adv Virus Res. 2019;103:33-70. doi: 10.1016/bs.aivir.2018.09.003. Epub 2018 Nov 28. Adv Virus Res. 2019. PMID: 30635077 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clocking out: modeling phage-induced lysis of Escherichia coli.J Bacteriol. 2007 Jul;189(13):4749-55. doi: 10.1128/JB.00392-07. Epub 2007 Apr 27. J Bacteriol. 2007. PMID: 17468251 Free PMC article.
-
Holins: the protein clocks of bacteriophage infections.Annu Rev Microbiol. 2000;54:799-825. doi: 10.1146/annurev.micro.54.1.799. Annu Rev Microbiol. 2000. PMID: 11018145 Review.
Cited by
-
Continuous Wave Electron Paramagnetic Resonance Spectroscopy Reveals the Structural Topology and Dynamic Properties of Active Pinholin S2168 in a Lipid Bilayer.J Phys Chem B. 2019 Sep 26;123(38):8048-8056. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcb.9b06480. Epub 2019 Sep 16. J Phys Chem B. 2019. PMID: 31478671 Free PMC article.
-
Functional Dissection of P1 Bacteriophage Holin-like Proteins Reveals the Biological Sense of P1 Lytic System Complexity.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Apr 11;23(8):4231. doi: 10.3390/ijms23084231. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35457047 Free PMC article.
-
Phage spanins: diversity, topological dynamics and gene convergence.BMC Bioinformatics. 2018 Sep 15;19(1):326. doi: 10.1186/s12859-018-2342-8. BMC Bioinformatics. 2018. PMID: 30219026 Free PMC article.
-
Evolutionary dominance of holin lysis systems derives from superior genetic malleability.Microbiology (Reading). 2008 Jun;154(Pt 6):1710-1718. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.2008/016956-0. Microbiology (Reading). 2008. PMID: 18524925 Free PMC article.
-
Conformational Differences Are Observed for the Active and Inactive Forms of Pinholin S21 Using DEER Spectroscopy.J Phys Chem B. 2020 Dec 17;124(50):11396-11405. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcb.0c09081. Epub 2020 Dec 8. J Phys Chem B. 2020. PMID: 33289567 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Barenboim, M., C.-Y. Chang, F. dib Hajj, and R. Young. 1999. Characterization of the dual start motif of a class II holin gene. Mol. Microbiol. 32:715-727. - PubMed
-
- Bull, J. J., D. W. Pfennig, and I. N. Wang. 2004. Genetic details, optimization and phage life histories. Trends Ecol. Evol. 19:76-82. - PubMed
-
- Delisa, M. P., P. Samuelson, T. Palmer, and G. Georgiou. 2002. Genetic analysis of the twin arginine translocator secretion pathway in bacteria. J. Biol. Chem. 277:29825-29831. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

