Impact of environmental and genetic factors on biofilm formation by the probiotic strain Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG
- PMID: 17827316
- PMCID: PMC2074970
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.01393-07
Impact of environmental and genetic factors on biofilm formation by the probiotic strain Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG
Abstract
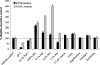
Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG (ATCC 53103) is one of the clinically best-studied probiotic organisms. Moreover, L. rhamnosus GG displays very good in vitro adherence to epithelial cells and mucus. Here, we report that L. rhamnosus GG is able to form biofilms on abiotic surfaces, in contrast to other strains of the Lactobacillus casei group tested under the same conditions. Microtiter plate biofilm assays indicated that in vitro biofilm formation by L. rhamnosus GG is strongly modulated by culture medium factors and conditions related to the gastrointestinal environment, including low pH; high osmolarity; and the presence of bile, mucins, and nondigestible polysaccharides. Additionally, phenotypic analysis of mutants affected in exopolysaccharides (wzb), lipoteichoic acid (dltD), and central metabolism (luxS) showed their relative importance in biofilm formation by L. rhamnosus GG.
Figures

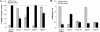


Similar articles
-
Functional analysis of luxS in the probiotic strain Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG reveals a central metabolic role important for growth and biofilm formation.J Bacteriol. 2007 Feb;189(3):860-71. doi: 10.1128/JB.01394-06. Epub 2006 Nov 10. J Bacteriol. 2007. PMID: 17098890 Free PMC article.
-
Functional analysis of D-alanylation of lipoteichoic acid in the probiotic strain Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2007 Jun;73(11):3595-604. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02083-06. Epub 2007 Apr 13. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2007. PMID: 17434999 Free PMC article.
-
AI-2/LuxS Quorum Sensing System Promotes Biofilm Formation of Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG and Enhances the Resistance to Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli in Germ-Free Zebrafish.Microbiol Spectr. 2022 Aug 31;10(4):e0061022. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.00610-22. Epub 2022 Jun 14. Microbiol Spectr. 2022. PMID: 35700135 Free PMC article.
-
Lactobacillus rhamnosus sepsis associated with probiotic therapy in an extremely preterm infant: Pathogenesis and a review for clinicians.J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2021 Aug;54(4):575-580. doi: 10.1016/j.jmii.2020.03.029. Epub 2020 Apr 3. J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2021. PMID: 32307246 Review.
-
Towards a better understanding of Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG--host interactions.Microb Cell Fact. 2014 Aug 29;13 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S7. doi: 10.1186/1475-2859-13-S1-S7. Epub 2014 Aug 29. Microb Cell Fact. 2014. PMID: 25186587 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Effect of Biofilm Formation by Lactobacillus plantarum on the Malolactic Fermentation in Model Wine.Foods. 2020 Jun 17;9(6):797. doi: 10.3390/foods9060797. Foods. 2020. PMID: 32560415 Free PMC article.
-
Proteomic studies on lactic acid bacteria: A review.Biochem Biophys Rep. 2018 May 4;14:140-148. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrep.2018.04.009. eCollection 2018 Jul. Biochem Biophys Rep. 2018. Retraction in: Biochem Biophys Rep. 2019 Sep 27;20:100689. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrep.2019.100689. PMID: 29872746 Free PMC article. Retracted. Review.
-
Genotypic and phenotypic diversity of Lactobacillus rhamnosus clinical isolates, their comparison with strain GG and their recognition by complement system.PLoS One. 2017 May 11;12(5):e0176739. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0176739. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28493885 Free PMC article.
-
Screening for probiotic characters in lactobacilli isolated from chickens revealed the intra-species diversity of Lactobacillus brevis.Anim Nutr. 2021 Mar;7(1):119-126. doi: 10.1016/j.aninu.2020.07.005. Epub 2020 Dec 28. Anim Nutr. 2021. PMID: 33997339 Free PMC article.
-
The Effect of Bacteria on the Stability of Microfluidic-Generated Water-in-Oil Droplet.Micromachines (Basel). 2022 Nov 25;13(12):2067. doi: 10.3390/mi13122067. Micromachines (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36557366 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Begley, M., C. G. Gahan, and C. Hill. 2005. The interaction between bacteria and bile. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 29:625-651. - PubMed
-
- Boekhorst, J., Q. Helmer, M. Kleerebezem, and R. J. Siezen. 2006. Comparative analysis of proteins with a mucus-binding domain found exclusively in lactic acid bacteria. Microbiology 152:273-280. - PubMed
-
- Bouazzaoui, K., and G. LaPointe. 2006. Use of antisense RNA to modulate glycosyltransferase gene expression and exopolysaccharide molecular mass in Lactobacillus rhamnosus. J. Microbiol. Methods 65:216-225. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

