Multiple modes of chromatin configuration at natural meiotic recombination hot spots in fission yeast
- PMID: 17827346
- PMCID: PMC2168419
- DOI: 10.1128/EC.00246-07
Multiple modes of chromatin configuration at natural meiotic recombination hot spots in fission yeast
Abstract
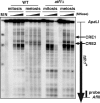
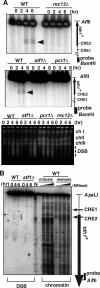
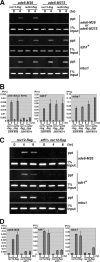
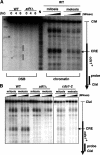
The ade6-M26 meiotic recombination hot spot of fission yeast is defined by a cyclic AMP-responsive element (CRE)-like heptanucleotide sequence, 5'-ATGACGT-3', which acts as a binding site for the Atf1/Pcr1 heterodimeric transcription factor required for hot spot activation. We previously demonstrated that the local chromatin around the M26 sequence motif alters to exhibit higher sensitivity to micrococcal nuclease before the initiation of meiotic recombination. In this study, we have examined whether or not such alterations in chromatin occur at natural meiotic DNA double-strand break (DSB) sites in Schizosaccharomyces pombe. At one of the most prominent DSB sites, mbs1 (meiotic break site 1), the chromatin structure has a constitutively accessible configuration at or near the DSB sites. The establishment of the open chromatin state and DSB formation are independent of the CRE-binding transcription factor, Atf1. Analysis of the chromatin configuration at CRE-dependent DSB sites revealed both differences from and similarities to mbs1. For example, the tdh1+ locus, which harbors a CRE consensus sequence near the DSB site, shows a meiotically induced open chromatin configuration, similar to ade6-M26. In contrast, the cds1+ locus is similar to mbs1 in that it exhibits a constitutive open configuration. Importantly, Atf1 is required for the open chromatin formation in both tdh1+ and cds1+. These results suggest that CRE-dependent meiotic chromatin changes are intrinsic processes related to DSB formation in fission yeast meiosis. In addition, the results suggest that the chromatin configuration in natural meiotic recombination hot spots can be classified into at least three distinct categories: (i) an Atf1-CRE-independent constitutively open chromatin configuration, (ii) an Atf1-CRE-dependent meiotically induced open chromatin configuration, and (iii) an Atf1-CRE-dependent constitutively open chromatin configuration.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Distinct chromatin modulators regulate the formation of accessible and repressive chromatin at the fission yeast recombination hotspot ade6-M26.Mol Biol Cell. 2008 Mar;19(3):1162-73. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e07-04-0377. Epub 2008 Jan 16. Mol Biol Cell. 2008. PMID: 18199689 Free PMC article.
-
Correlation of Meiotic DSB Formation and Transcription Initiation Around Fission Yeast Recombination Hotspots.Genetics. 2017 Jun;206(2):801-809. doi: 10.1534/genetics.116.197954. Epub 2017 Apr 10. Genetics. 2017. PMID: 28396503 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of histone acetylation and chromatin remodeling factor in a meiotic recombination hotspot.EMBO J. 2004 Apr 21;23(8):1792-803. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600138. Epub 2004 Feb 26. EMBO J. 2004. PMID: 14988732 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation Mechanisms of Meiotic Recombination Revealed from the Analysis of a Fission Yeast Recombination Hotspot ade6-M26.Biomolecules. 2022 Nov 26;12(12):1761. doi: 10.3390/biom12121761. Biomolecules. 2022. PMID: 36551189 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The conserved histone variant H2A.Z illuminates meiotic recombination initiation.Curr Genet. 2018 Oct;64(5):1015-1019. doi: 10.1007/s00294-018-0825-9. Epub 2018 Mar 16. Curr Genet. 2018. PMID: 29549582 Review.
Cited by
-
Acetylated Histone H3K9 is associated with meiotic recombination hotspots, and plays a role in recombination redundantly with other factors including the H3K4 methylase Set1 in fission yeast.Nucleic Acids Res. 2013 Apr 1;41(6):3504-17. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkt049. Epub 2013 Feb 4. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013. PMID: 23382177 Free PMC article.
-
Evolutionarily diverse determinants of meiotic DNA break and recombination landscapes across the genome.Genome Res. 2014 Oct;24(10):1650-64. doi: 10.1101/gr.172122.114. Epub 2014 Jul 14. Genome Res. 2014. PMID: 25024163 Free PMC article.
-
Histone Chaperone Asf1 Is Required for the Establishment of Repressive Chromatin in Schizosaccharomyces pombe fbp1 Gene Repression.Mol Cell Biol. 2018 Aug 28;38(18):e00194-18. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00194-18. Print 2018 Sep 15. Mol Cell Biol. 2018. PMID: 29967244 Free PMC article.
-
Diverse DNA Sequence Motifs Activate Meiotic Recombination Hotspots Through a Common Chromatin Remodeling Pathway.Genetics. 2019 Nov;213(3):789-803. doi: 10.1534/genetics.119.302679. Epub 2019 Sep 11. Genetics. 2019. PMID: 31511300 Free PMC article.
-
Initiation of meiotic recombination in mammals.Genes (Basel). 2010 Dec 22;1(3):521-49. doi: 10.3390/genes1030521. Genes (Basel). 2010. PMID: 24710101 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cervantes, M. D., J. A. Farah, and G. R. Smith. 2000. Meiotic DNA breaks associated with recombination in S. pombe. Mol. Cell 5:883-888. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

