Effects and mechanisms of electroacupuncture at PC6 on frequency of transient lower esophageal sphincter relaxation in cats
- PMID: 17828819
- PMCID: PMC4611766
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i36.4873
Effects and mechanisms of electroacupuncture at PC6 on frequency of transient lower esophageal sphincter relaxation in cats
Abstract
Aim: To investigate the effects of electroacupuncture (EA) at neiguan (PC6) on gastric distention-induced transient lower esophageal sphincter relaxations (TLESRs) and discuss the mechanisms of this treatment.
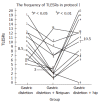
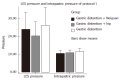
Methods: Protocol I: Twelve healthy cats underwent gastric distention for 60 min on the first day. Electrical acupoint stimulation was applied at the neiguan or a sham point on the hip in randomized order before gastric distention, on the third day and fifth day. Those cats that underwent EA at neiguan on the fifth day were named "Neiguan Group" and the cats that underwent EA at a sham acupoint on the fifth day were named "Sham Group" (control group). During the experiment the frequency of TLESRs and lower esophageal sphincter (LES) pressure were observed by a perfused sleeve assembly. Plasma levels of gastrin (GAS) and motilin (MTL) were determined by radioimmunoassay. Nitrite/nitrate concentration in plasma and tissues were measured by Griess reagent. The nuclei in the brain stem were observed by immunohistochemistry method of c-Fos and NADPH-d dyeing. Protocol II: Thirty six healthy cats were divided into 6 groups randomly. We gave saline (2 mL iv. control group), phaclofen (5 mg/kg iv. GABA-B antagonist), cholecystokinin octapeptide (CCK-8) (1 microg/kg per hour iv.), L-Arginine (200 mg/kg iv.), naloxone (2.5 micromol/kg iv.) and tacrine (5.6 mg/kg ip. cholinesterase inhibitor) respectively before EA at Neiguan and gastric distention. And the frequencies of TLESRs in experimental groups were compared with the control group.
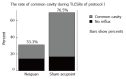
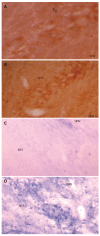
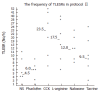
Results: Protocol I: Not only the frequency of gastric distention-induced TLESR in 60 min but also the rate of common cavity during TLESRs were significantly decreased by EA at neiguan compared to that of sham acupoint stimulation. C-Fos immunoreactivity and NOS reactivity in the solitarius (NTS) and dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus (DMV) were significantly decreased by EA at neiguan compared to that of the sham group. However, the positive nuclei of C-Fos and NOS in reticular formation of the medulla (RFM) were increased by EA at neiguan. Protocol II: The inhibited effect of EA at neiguan on TLESR's frequency was completely restored by pretreatment with CCK (23.5/h vs 4.5/h, P < 0.05), L-arginine (17.5/h vs 4.5/h, P < 0.05) and naloxone(12/h vs 4.5/h, P < 0.05). On the contrary, phaclofen (6/h vs 4.5/h, P > 0.05) and tacrine (9.5/h vs 4.5/h, P > 0.05) did not influence it.
Conclusion: Electric acupoint stimulation at Neiguan significantly inhibits the frequency of TLESR and the rate of common cavity during TLESR in cats. This effect appears to act on the brain stem, and may be mediated through nitric oxide (NO), CCK-A receptor and mu-opioid receptors. But the GABAB receptor and acetylcholine may not be involved in it.
Figures



Similar articles
-
[Electroacupuncture at "Zusanli"(ST 36) can inhibit frequencies of transient lower esophageal sphincter relaxation induced by gastric distention in cats].Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2011 Dec;36(6):423-7. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2011. PMID: 22379788 Chinese.
-
Electroacupuncture at PC6 or ST36 Influences the Effect of Tacrine on the Motility of Esophagus.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2014;2014:263489. doi: 10.1155/2014/263489. Epub 2014 Apr 7. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2014. PMID: 24808917 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of transient lower esophageal sphincter relaxations by electrical acupoint stimulation.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2005 Aug;289(2):G197-201. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00023.2005. Epub 2005 Apr 14. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2005. PMID: 15831714 Clinical Trial.
-
The lower esophageal sphincter.Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2011 Sep;23(9):819-30. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2982.2011.01738.x. Epub 2011 Jun 29. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2011. PMID: 21711416 Review.
-
[Transient lower esophageal sphincter relaxation and the related esophageal motor activities].Korean J Gastroenterol. 2012 Mar;59(3):205-10. doi: 10.4166/kjg.2012.59.3.205. Korean J Gastroenterol. 2012. PMID: 22460568 Review. Korean.
Cited by
-
Thread-embedding acupuncture may improve symptom resolution in patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease: A randomized controlled trial.Integr Med Res. 2023 Sep;12(3):100971. doi: 10.1016/j.imr.2023.100971. Epub 2023 Jul 7. Integr Med Res. 2023. PMID: 37637187 Free PMC article.
-
Electroacupuncture Improves Choroidal Blood Flow to Inhibit the Development of Lens-Induced Myopia in Guinea Pigs.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022 Jun 24;2022:3286583. doi: 10.1155/2022/3286583. eCollection 2022. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022. PMID: 35783515 Free PMC article.
-
Electroacupuncture for patients with irritable bowel syndrome: A systematic review and meta-analysis protocol.Medicine (Baltimore). 2018 Aug;97(31):e11627. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000011627. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018. PMID: 30075541 Free PMC article.
-
Effectiveness and safety of acupuncture for cancer-related hiccups: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Neurol. 2024 Dec 11;15:1480656. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2024.1480656. eCollection 2024. Front Neurol. 2024. PMID: 39722696 Free PMC article.
-
Electroacupuncture to treat gastroesophageal reflux disease: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial.Trials. 2016 May 17;17(1):246. doi: 10.1186/s13063-016-1371-8. Trials. 2016. PMID: 27188910 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Mittal RK, McCallum RW. Characteristics and frequency of transient relaxations of the lower esophageal sphincter in patients with reflux esophagitis. Gastroenterology. 1988;95:593–599. - PubMed
-
- Holloway RH, Hongo M, Berger K, McCallum RW. Gastric distention: a mechanism for postprandial gastroesophageal reflux. Gastroenterology. 1985;89:779–784. - PubMed
-
- Lee KJ, Vos R, Janssens J, Tack J. Differential effects of baclofen on lower oesophageal sphincter pressure and proximal gastric motility in humans. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2003;18:199–207. - PubMed
-
- Boulant J, Fioramonti J, Dapoigny M, Bommelaer G, Bueno L. Cholecystokinin and nitric oxide in transient lower esophageal sphincter relaxation to gastric distention in dogs. Gastroenterology. 1994;107:1059–1066. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

