Distinct roles for intra- and extracellular siderophores during Aspergillus fumigatus infection
- PMID: 17845073
- PMCID: PMC1971116
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.0030128
Distinct roles for intra- and extracellular siderophores during Aspergillus fumigatus infection
Abstract
Siderophore biosynthesis by the highly lethal mould Aspergillus fumigatus is essential for virulence, but non-existent in humans, presenting a rare opportunity to strategize therapeutically against this pathogen. We have previously demonstrated that A. fumigatus excretes fusarinine C and triacetylfusarinine C to capture extracellular iron, and uses ferricrocin for hyphal iron storage. Here, we delineate pathways of intra- and extracellular siderophore biosynthesis and show that A. fumigatus synthesizes a developmentally regulated fourth siderophore, termed hydroxyferricrocin, employed for conidial iron storage. By inactivation of the nonribosomal peptide synthetase SidC, we demonstrate that the intracellular siderophores are required for germ tube formation, asexual sporulation, resistance to oxidative stress, catalase A activity, and virulence. Restoration of the conidial hydroxyferricrocin content partially rescues the virulence of the apathogenic siderophore null mutant Delta sidA, demonstrating an important role for the conidial siderophore during initiation of infection. Abrogation of extracellular siderophore biosynthesis following inactivation of the acyl transferase SidF or the nonribosomal peptide synthetase SidD leads to complete dependence upon reductive iron assimilation for growth under iron-limiting conditions, partial sensitivity to oxidative stress, and significantly reduced virulence, despite normal germ tube formation. Our findings reveal distinct cellular and disease-related roles for intra- and extracellular siderophores during mammalian Aspergillus infection.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



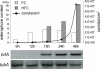



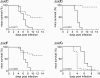


References
-
- Weinberg ED. The role of iron in protozoan and fungal infectious diseases. J Eukaryot Microbiol. 1999;46:231–238. - PubMed
-
- Weiss G. Iron and immunity: A double-edged sword. Eur J Clin Invest. 2002;32(Suppl 1):70–78. - PubMed
-
- Hersleth HP, Ryde U, Rydberg P, Gorbitz CH, Andersson KK. Structures of the high-valent metal-ion haem-oxygen intermediates in peroxidases, oxygenases and catalases. J Inorg Biochem. 2006;100:460–476. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

