Association of the microsatellite in the 3' untranslated region of the CD154 gene with rheumatoid arthritis in females from a Spanish cohort: a case-control study
- PMID: 17845713
- PMCID: PMC2212561
- DOI: 10.1186/ar2288
Association of the microsatellite in the 3' untranslated region of the CD154 gene with rheumatoid arthritis in females from a Spanish cohort: a case-control study
Abstract
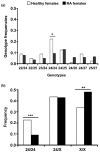
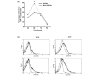
CD40-CD154 interaction is an important mediator of inflammation and has been implicated in T helper type 1-mediated autoimmune diseases including rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Linkage studies have shown association of markers in the proximity of the CD154 gene. In the present work we investigated whether specific allele variants of the microsatellite in the 3' UTR of the CD154 gene might modulate the risk of RA. The study, in a case-control setting, included 189 patients and 150 healthy controls from the Canary Islands, Spain. The 24CAs allele was less represented in female patients than in controls (0.444 in controls versus 0.307 in patients, P = 0.006, odds ratio (OR) 0.556, 95% confidence interval (CI) 0.372 to 0.831) but not in males (0.414 versus 0.408), and only when homozygous (P = 0.012; OR 0.35, 95% CI 0.16 to 0.77). We also verified that CD154 association with RA was independent of human leukocyte antigen (HLA) phenotype. A further functional study showed that after stimulation anti-CD3, CD154 mRNA was more stable in CD4+ T lymphocytes from patients with RA bearing the 24CAs allele (mRNA half-life 208 minutes) than in patients without the 24CAs allele (109 minutes, P = 0.009). However, a lower percentage of CD154+CD4+ T lymphocytes was seen in freshly isolated peripheral blood mononuclear cells from patients carrying 24CAs alleles (mean 4.28 versus 8.12; P = 0.033), and also in CD4+ T lymphocytes stimulated with anti-CD3 (median 29.40 versus 47.60; P = 0.025). These results were concordant with the smaller amounts of CD154 mRNA isolated from stimulated T lymphocytes with 24CAs alleles. The CD154 microsatellite therefore seems to affect the expression of the gene in a complex manner that implies not only mRNA stability. These data suggest that the CD154 microsatellite contributes to the regulation of mRNA and protein expression, although further studies will be necessary to elucidate its role in disease predisposition.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Post-transcriptional regulation in lymphocytes: the case of CD154.RNA Biol. 2009 Jul-Aug;6(3):259-65. doi: 10.4161/rna.6.3.8581. Epub 2009 Jul 29. RNA Biol. 2009. PMID: 19395873 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Peripheral blood lymphocytes in SLE--hyperexpression of CD154 on T and B lymphocytes and increased number of double negative T cells.J Autoimmun. 1998 Oct;11(5):471-5. doi: 10.1006/jaut.1998.0213. J Autoimmun. 1998. PMID: 9802931
-
Association of PTPN22 single nucleotide polymorphism with rheumatoid arthritis but not with allergic asthma.Eur J Hum Genet. 2007 Oct;15(10):1043-8. doi: 10.1038/sj.ejhg.5201879. Epub 2007 Jun 20. Eur J Hum Genet. 2007. PMID: 17579671
-
Tumor necrosis factor-alpha microsatellite polymorphism association with rheumatoid arthritis in Indian patients.Arch Med Res. 2005 Sep-Oct;36(5):555-9. doi: 10.1016/j.arcmed.2005.03.035. Arch Med Res. 2005. PMID: 16099338
-
Functional significance of microsatellite markers.Medicina (Kaunas). 2013;49(12):505-9. Medicina (Kaunas). 2013. PMID: 24858989 Review.
Cited by
-
A GA microsatellite in the Fli1 promoter modulates gene expression and is associated with systemic lupus erythematosus patients without nephritis.Arthritis Res Ther. 2010;12(6):R212. doi: 10.1186/ar3189. Epub 2010 Nov 18. Arthritis Res Ther. 2010. PMID: 21087477 Free PMC article.
-
Are polymorphisms of the immunoregulatory factor CD40LG implicated in acute transfusion reactions?Sci Rep. 2014 Nov 28;4:7239. doi: 10.1038/srep07239. Sci Rep. 2014. PMID: 25430087 Free PMC article.
-
Post-transcriptional regulation in lymphocytes: the case of CD154.RNA Biol. 2009 Jul-Aug;6(3):259-65. doi: 10.4161/rna.6.3.8581. Epub 2009 Jul 29. RNA Biol. 2009. PMID: 19395873 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CD40 and autoimmunity: the dark side of a great activator.Semin Immunol. 2009 Oct;21(5):293-300. doi: 10.1016/j.smim.2009.05.012. Semin Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19595612 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Levels of human platelet-derived soluble CD40 ligand depend on haplotypes of CD40LG-CD40-ITGA2.Sci Rep. 2016 Apr 20;6:24715. doi: 10.1038/srep24715. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27094978 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Decker JL, Malone DG, Haraoui B, Wahl SM, Schrieber L, Klippel JH, Steinberg AD, Wilder RL. NIH conference. Rheumatoid arthritis: evolving concepts of pathogenesis and treatment. Ann Intern Med. 1984;101:810–824. - PubMed
-
- van der Helm-van Mil AH, Wesoly JZ, Huizinga TW. Understanding the genetic contribution to rheumatoid arthritis. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2005;17:299–304. doi: 10.1097/01.bor.0000160780.13012.be. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

