Manganese-induced potentiation of in vitro proinflammatory cytokine production by activated microglial cells is associated with persistent activation of p38 MAPK
- PMID: 17845838
- PMCID: PMC2231510
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tiv.2007.07.004
Manganese-induced potentiation of in vitro proinflammatory cytokine production by activated microglial cells is associated with persistent activation of p38 MAPK
Abstract
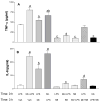
Previous studies that investigated the role of inflammation in the neurotoxicity of manganese (Mn) found that Mn enhanced the production of inflammogen (lipopolysaccharide; LPS)-induced proinflammatory cytokines such as IL-6 and TNF-alpha. Although we have shown that the enhanced cytokine production occurs via a NF-kappaB-dependent mechanism, the role of upstream kinases in this Mn-induced enhancement has not been explored. As other studies have demonstrated that p38 mitogen activated protein kinase (p38) is necessary for LPS-induced, NF-kappaB-dependent expression of proinflammatory cytokines, we hypothesized that Mn enhancement of LPS-induced production of IL-6 and TNF-alpha may be associated with p38 activation and conducted a series of experiments to address our hypothesis. We found that pre-treatment of microglial cells with a p38-inhibitor (SB203580) prevented Mn+LPS-induced production of IL-6 and TNF-alpha. Moreover, potentiation of IL-6 and TNF-alpha production, which occurred in both concurrent and sequential (3h apart) exposures to Mn and LPS, was inhibited by inhibition of p38. Additionally, Mn exposure enhanced the phosphorylation and activity of p38 and this effect was persistent. Although p38 activity declined over time LPS-exposed cells, it persisted in cells exposed to Mn or Mn+LPS. Thus, the increased production of proinflammatory cytokines by LPS-activated microglia exposed to Mn is associated with increased and persistent activation of p38.
Figures



References
-
- Aschner M, Aschner JL. Manganese neurotoxicity: Cellular effects and blood-brain barrier transport. Neuroscience Biobehavior Review. 1991;15:334–340. - PubMed
-
- Bae JH, Jang BC, Suh SI, Ha E, Baik HH, Kim SS, Lee MY, Shin DH. Manganese induces inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) expression via activation of both MAP kinase and PI3K/Akt pathways in BV2 microglial cells. Neuroscience Letters. 2006;398:151–154. - PubMed
-
- Bhat NR, Zhang P, Lee JC, Hogan EL. Extracellular signal-regulated kinase and p38 subgroups of mitogen-activated protein kinases regulate inducible nitric oxide synthase and tumor necrosis factor-a gene expression in endotoxin-stimulated primary glial cultures. Journal of Neuroscience. 1998;18:1633–1641. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Carter AB, Knudtson KL, Monick MM, Hunninghake GW. The p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase is required for NF-κB-dependent gene expression. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 1999;274:30858–30863. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

