Neurofascin as a novel target for autoantibody-mediated axonal injury
- PMID: 17846150
- PMCID: PMC2118456
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20071053
Neurofascin as a novel target for autoantibody-mediated axonal injury
Abstract
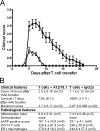
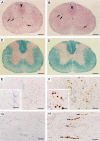
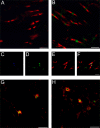
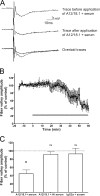
Axonal injury is considered the major cause of disability in patients with multiple sclerosis (MS), but the underlying effector mechanisms are poorly understood. Starting with a proteomics-based approach, we identified neurofascin-specific autoantibodies in patients with MS. These autoantibodies recognize the native form of the extracellular domains of both neurofascin 186 (NF186), a neuronal protein concentrated in myelinated fibers at nodes of Ranvier, and NF155, the oligodendrocyte-specific isoform of neurofascin. Our in vitro studies with hippocampal slice cultures indicate that neurofascin antibodies inhibit axonal conduction in a complement-dependent manner. To evaluate whether circulating antineurofascin antibodies mediate a pathogenic effect in vivo, we cotransferred these antibodies with myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein-specific encephalitogenic T cells to mimic the inflammatory pathology of MS and breach the blood-brain barrier. In this animal model, antibodies to neurofascin selectively targeted nodes of Ranvier, resulting in deposition of complement, axonal injury, and disease exacerbation. Collectively, these results identify a novel mechanism of immune-mediated axonal injury that can contribute to axonal pathology in MS.
Figures

References
-
- Steinman, L. 2001. Multiple sclerosis: a two-stage disease. Nat. Immunol. 2:762–764. - PubMed
-
- Hauser, S.L., and J.R. Oksenberg. 2006. The neurobiology of multiple sclerosis: genes, inflammation, and neurodegeneration. Neuron. 52:61–76. - PubMed
-
- Trapp, B.D., R. Ransohoff, and R. Rudick. 1999. Axonal pathology in multiple sclerosis: relationship to neurologic disability. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 12:295–302. - PubMed
-
- Ferguson, B., M.K. Matyszak, M.M. Esiri, and V.H. Perry. 1997. Axonal damage in acute multiple sclerosis lesions. Brain. 120:393–399. - PubMed
-
- Trapp, B.D., J. Peterson, R.M. Ransohoff, R. Rudick, S. Mork, and L. Bo. 1998. Axonal transection in the lesions of multiple sclerosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 338:278–285. - PubMed

