High-density lipoprotein protects macrophages from oxidized low-density lipoprotein-induced apoptosis by promoting efflux of 7-ketocholesterol via ABCG1
- PMID: 17846428
- PMCID: PMC1986618
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0704602104
High-density lipoprotein protects macrophages from oxidized low-density lipoprotein-induced apoptosis by promoting efflux of 7-ketocholesterol via ABCG1
Abstract
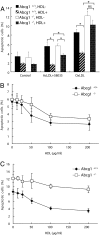
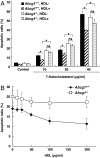
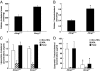
Oxidized sterols consumed in the diet or formed on low-density lipoprotein (LDL) are toxic to endothelial cells and macrophages and are thought to have a central role in promoting atherogenesis. The ATP-binding cassette transporter ABCG1 was recently shown to promote efflux of cholesterol from macrophages to high-denisty lipoprotein (HDL). We show that HDL protects macrophages from apoptosis induced by loading with free cholesterol or oxidized LDL. The protective effect of HDL was reduced in Abcg1(-/-) macrophages, especially after loading with oxidized LDL. Similarly, HDL exerted a protective effect against apoptosis induced by 7-ketocholesterol, the major oxysterol present in oxidized LDL and atherosclerotic lesions, in Abcg1(+/+), but not in Abcg1(-/-) macrophages. In transfected 293 cells, efflux of 7-ketocholesterol and related oxysterols was completely dependent on expression of ABCG1 and the presence of HDL in media. In contrast, ABCA1 and apoA-1 did not stimulate the efflux of 7-ketocholesterol into media. HDL stimulated the efflux of 7-ketocholesterol from Abcg1(+/+), but not from Abcg1(-/-) macrophages. In Abcg1(-/-) mice fed a high-cholesterol diet, plasma levels of 7-ketocholesterol were reduced, whereas their macrophages accumulated 7-ketocholesterol. These findings indicate a specific role for ABCG1 in promoting efflux of 7-ketocholesterol and related oxysterols from macrophages onto HDL and in protecting these cells from oxysterol-induced cytotoxicity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
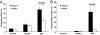
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

