A defect in the ionotropic glutamate receptor 6 gene (GRIK2) is associated with autosomal recessive mental retardation
- PMID: 17847003
- PMCID: PMC2227928
- DOI: 10.1086/521275
A defect in the ionotropic glutamate receptor 6 gene (GRIK2) is associated with autosomal recessive mental retardation
Abstract
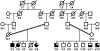
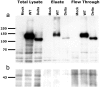
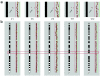
Nonsyndromic mental retardation is one of the most important unresolved problems in genetic health care. Autosomal forms are far more common than X-linked forms, but, in contrast to the latter, they are still largely unexplored. Here, we report a complex mutation in the ionotropic glutamate receptor 6 gene (GRIK2, also called "GLUR6") that cosegregates with moderate-to-severe nonsyndromic autosomal recessive mental retardation in a large, consanguineous Iranian family. The predicted gene product lacks the first ligand-binding domain, the adjacent transmembrane domain, and the putative pore loop, suggesting a complete loss of function of the GLU(K6) protein, which is supported by electrophysiological data. This finding provides the first proof that GLU(K6) is indispensable for higher brain functions in humans, and future studies of this and other ionotropic kainate receptors will shed more light on the pathophysiology of mental retardation.
Figures


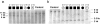

References
Web Resource
-
- Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM), http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Omim/ (for neurotrypsin, cereblon, CC2D1A, MRT6, GRIK2, and fragile X syndrome)
References
-
- Basel-Vanagaite L, Attia R, Yahav M, Ferland RJ, Anteki L, Walsh CA, Olender T, Straussberg R, Magal N, Taub E, et al (2006) The CC2D1A, a member of a new gene family with C2 domains, is involved in autosomal recessive non-syndromic mental retardation. J Med Genet 43:203–210 10.1136/jmg.2005.035709 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Najmabadi H, Motazacker MM, Garshasbi M, Kahrizi K, Tzschach A, Chen W, Behjati F, Hadavi V, Nieh SE, Abedini SS, et al (2006) Homozygosity mapping in consanguineous families reveals extreme heterogeneity of non-syndromic autosomal recessive mental retardation and identifies 8 novel gene loci. Hum Genet 121:43–48 10.1007/s00439-006-0292-0 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Rozen S, Skaletsky H (2000) Primer3 on the WWW for general users and for biologist programmers. Methods Mol Biol 132:365–386 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

