Hexagon TB for the rapid diagnosis of lung TBC in praxis
- PMID: 17848145
- PMCID: PMC5736111
- DOI: 10.17305/bjbms.2007.3047
Hexagon TB for the rapid diagnosis of lung TBC in praxis
Abstract
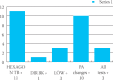
Hexagon TB is intended for the rapid diagnostics of tuberculosis. Tuberculosis is a contagious and epidemic disease. According to the data published by WHO, 3-4 millions of patients are diagnosed with this disease annually. In 2004, 107 new cases were discovered in the area of Tuzla Municipality. Annual incidence of this disease is 62,9 per 100 000 inhabitants in Bosnia and Herzegovina; 28,9 in Slovenia; 33,2 in FYRM; 48,5 in Croatia; 41,8 in Serbia and Montenegro. Western European countries have a rather low rate of the disease--5-10 cases per 100 000 inhabitants. Efficiency of Hexagon TB examination method was tested on 100 patients. The subjects were patients with clinical symptoms of active TBC infection, persons who were in contact with TBC patients and persons earlier cured of TBC. All the subjects were tested with Hexagon TB, and the results were compared against lungs X-rays and sputum test for BK and LOW. Hexagon TB is intended for rapid, qualitative detection of IgG, IgA, IgM antibodies against M. tuberculosis and mycobacterium in human serum, plasma or whole blood as an aid in the early diagnostics of tuberculosis infections for professional use. Hexagon TB was positive in 11 of the examined patients. 10 patients had changes suggesting TBC. 1 patient was directly positive for BK and 3 patients were positive for LOW. Of all the examined patients, 3 were positive for all tests positive. According to our results, Hexagon TB has significant importance in practice of rapid TBC diagnostics compared to lungs X-ray and examination of sputum for BK and LOW.
Figures
References
-
- Nurkić M. Mikobakterije. Tuzla: Klinički značaj i metode; 2000.
-
- Dodig S, Čepelak I. Medicinsko-biokemiske pretrage u pul-mologiji. Zagreb: Školska knjiga; 1997.
-
- Popovac D. Bolesti pluća. V dopunjeno izdanje Beograd. 1999
-
- Dizdarević Z. Nacionalni program za tuberkulozu Bosne i Hercegovine, Ministarstvo zdravlja Federacije Bosne i Hercegovine, Print M. Sarajevo. 1998:15–21.
-
- Terr A.I. Multiple chemical sensitivities. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1994;94(2):362–366. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous