Structural insights into the Slit-Robo complex
- PMID: 17848514
- PMCID: PMC1975871
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0705310104
Structural insights into the Slit-Robo complex
Abstract
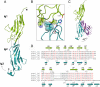
Slits are large multidomain leucine-rich repeat (LRR)-containing proteins that provide crucial guidance cues in neuronal and vascular development. More recently, Slits have been implicated in heart morphogenesis, angiogenesis, and tumor metastasis. Slits are ligands for the Robo (Roundabout) receptors, which belong to the Ig superfamily of transmembrane signaling molecules. The Slit-Robo interaction is mediated by the second LRR domain of Slit and the two N-terminal Ig domains of Robo, but the molecular details of this interaction and how it induces signaling remain unclear. Here we describe the crystal structures of the second LRR domain of human Slit2 (Slit2 D2), the first two Ig domains of its receptor Robo1 (Ig1-2), and the minimal complex between these proteins (Slit2 D2-Robo1 Ig1). Slit2 D2 binds with its concave surface to the side of Ig1 with electrostatic and hydrophobic contact regions mediated by residues that are conserved in other family members. Surface plasmon resonance experiments and a mutational analysis of the interface confirm that Ig1 is the primary domain for binding Slit2. These structures provide molecular insight into Slit-Robo complex formation and will be important for the development of novel cancer therapeutics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

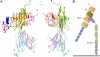
Similar articles
-
Structural and functional analysis of slit and heparin binding to immunoglobulin-like domains 1 and 2 of Drosophila Robo.J Biol Chem. 2008 Jun 6;283(23):16226-34. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M800688200. Epub 2008 Mar 20. J Biol Chem. 2008. PMID: 18359766 Free PMC article.
-
High structural resolution hydroxyl radical protein footprinting reveals an extended Robo1-heparin binding interface.J Biol Chem. 2015 Apr 24;290(17):10729-40. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.648410. Epub 2015 Mar 9. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 25752613 Free PMC article.
-
Structural insight into Slit-Robo signalling.Biochem Soc Trans. 2008 Apr;36(Pt 2):251-6. doi: 10.1042/BST0360251. Biochem Soc Trans. 2008. PMID: 18363568 Review.
-
Production of Slit2 LRR domains in mammalian cells for structural studies and the structure of human Slit2 domain 3.Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2007 Sep;63(Pt 9):961-8. doi: 10.1107/S0907444907035470. Epub 2007 Aug 17. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2007. PMID: 17704564
-
Structure and Function of Roundabout Receptors.Subcell Biochem. 2019;93:291-319. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-28151-9_9. Subcell Biochem. 2019. PMID: 31939155 Review.
Cited by
-
In vivo functional analysis of Drosophila Robo1 immunoglobulin-like domains.Neural Dev. 2016 Aug 18;11(1):15. doi: 10.1186/s13064-016-0071-0. Neural Dev. 2016. PMID: 27539083 Free PMC article.
-
The transmembrane LRR protein DMA-1 promotes dendrite branching and growth in C. elegans.Nat Neurosci. 2011 Dec 4;15(1):57-63. doi: 10.1038/nn.2978. Nat Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 22138642 Free PMC article.
-
Temporal regulation of axonal repulsion by alternative splicing of a conserved microexon in mammalian Robo1 and Robo2.Elife. 2019 Aug 8;8:e46042. doi: 10.7554/eLife.46042. Elife. 2019. PMID: 31392959 Free PMC article.
-
The role of Slit-Robo signaling in the regulation of tissue barriers.Tissue Barriers. 2017 Apr 3;5(2):e1331155. doi: 10.1080/21688370.2017.1331155. Epub 2017 Jun 8. Tissue Barriers. 2017. PMID: 28598714 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The EBAX-type Cullin-RING E3 ligase and Hsp90 guard the protein quality of the SAX-3/Robo receptor in developing neurons.Neuron. 2013 Sep 4;79(5):903-16. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2013.06.035. Neuron. 2013. PMID: 24012004 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dickson BJ, Gilestro GF. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2006;22:651–675. - PubMed
-
- Garbe DS, Bashaw GJ. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2004;39:319–341. - PubMed
-
- Carmeliet P, Tessier-Lavigne M. Nature. 2005;436:193–200. - PubMed
-
- Fujiwara M, Ghazizadeh M, Kawanami O. Vasc Med. 2006;11:115–121. - PubMed
-
- Qian L, Liu J, Bodmer R. Curr Biol. 2005;15:2271–2278. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

