Activity-dependent regulation of h channel distribution in hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neurons
- PMID: 17848552
- PMCID: PMC2685032
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M703736200
Activity-dependent regulation of h channel distribution in hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neurons
Abstract
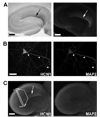
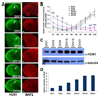
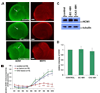
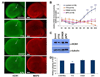
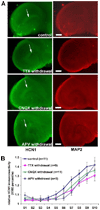
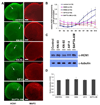
The hyperpolarization-activated cation current, I(h), plays an important role in regulating intrinsic neuronal excitability in the brain. In hippocampal pyramidal neurons, I(h) is mediated by h channels comprised primarily of the hyperpolarization-activated cyclic nucleotide-gated (HCN) channel subunits, HCN1 and HCN2. Pyramidal neuron h channels within hippocampal area CA1 are remarkably enriched in distal apical dendrites, and this unique distribution pattern is critical for regulating dendritic excitability. We utilized biochemical and immunohistochemical approaches in organotypic slice cultures to explore factors that control h channel localization in dendrites. We found that distal dendritic enrichment of HCN1 is first detectable at postnatal day 13, reaching maximal enrichment by the 3rd postnatal week. Interestingly we found that an intact entorhinal cortex, which projects to distal dendrites of CA1 but not area CA3, is critical for the establishment and maintenance of distal dendritic enrichment of HCN1. Moreover blockade of excitatory neurotransmission using tetrodotoxin, 6-cyano-7-nitroquinoxaline-2,3-dione, or 2-aminophosphonovalerate redistributed HCN1 evenly throughout the dendrite without significant changes in protein expression levels. Inhibition of calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II activity, but not p38 MAPK, also redistributed HCN1 in CA1 pyramidal neurons. We conclude that activation of ionotropic glutamate receptors by excitatory temporoammonic pathway projections from the entorhinal cortex establishes and maintains the distribution pattern of HCN1 in CA1 pyramidal neuron dendrites by activating calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II-mediated downstream signals.
Figures




References
-
- Lai HC, Jan LY. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2006;7:548–562. - PubMed
-
- Ludwig A, Zong X, Jeglitsch M, Hofmann F, Biel M. Nature. 1998;393:587–591. - PubMed
-
- Santoro B, Liu DT, Yao H, Bartsch D, Kandel ER, Siegelbaum SA, Tibbs GR. Cell. 1998;93:717–729. - PubMed
-
- Lorincz A, Notomi T, Tamas G, Shigemoto R, Nusser Z. Nat. Neurosci. 2002;5:1185–1193. - PubMed
-
- Notomi T, Shigemoto R. J. Comp. Neurol. 2004;471:241–276. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

